5Z-7-Oxozeaenol
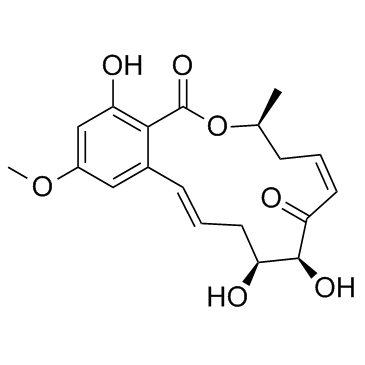
5Z-7-Oxozeaenol structure
|
Common Name | 5Z-7-Oxozeaenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 253863-19-3 | Molecular Weight | 362.37400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid suppress adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells via differential mechanisms.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 59(4) , 751-62, (2015) Dietary PUFAs modulate the progression of cardiovascular disease, but the underlying mechanisms within vascular cells remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the biological function and regulatory mechanisms of PUFAs in LPS-activated human ao... |
|
|
Flavonoids inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes and cytokine/chemokine production in human whole blood.
Inflammation 38(2) , 858-70, (2015) Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and the production of cytokines/chemokines are important targets for the modulation of the inflammatory response. Although a large variety of inhibitors of these pathways have been commercialized, some of those inhibitors present seve... |
|
|
Disruption of thioredoxin metabolism enhances the toxicity of transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) inhibition in KRAS-mutated colon cancer cells.
Redox Biol. 5 , 319-27, (2016) Transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) is critical for survival of many KRAS mutated colorectal cancer cells, and TAK1 inhibition with 5Z-7-oxozeaenol has been associated with oxidative stress leading to tumor cell killing. When SW 620 and HCT... |
|
|
NF-κB feedback control of JNK1 activation modulates TRPV1-induced increases in IL-6 and IL-8 release by human corneal epithelial cells.
Mol. Vis. 17 , 3137-46, (2011) The corneal wound healing response to an alkali burn results in dysregulated inflammation and opacity. Transient receptor potential vanilloid type1 (TRPV1) ion channel activation by such a stress contributes to this unfavorable outcome. Accordingly, we sought... |
|
|
The role of TAK1 expression in thyroid cancer.
Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8 , 14449-56, (2016) To investigate the expression, significance, and role of transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) in human thyroid cancer tissue.The data of 101 patients with thyroid cancer who underwent surgical treatment at our hospital from June 2001 to Marc... |
|
|
Role of tyrosine kinase-independent phosphorylation of EGFR with activating mutation in cisplatin-treated lung cancer cells.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 458(4) , 856-61, (2015) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation is one of the hallmarks of cancer progression and resistance to anticancer therapies, particularly non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLCs). In contrast to the canonical EGFR activation in which tyrosine residue... |
|
|
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase potentiates the apoptotic effect of berberine/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand combination therapy.
Oncol. Lett. 10 , 1907-1911, (2015) It was previously reported that berberine (BBR) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) exhibited a synergistic apoptotic effect on triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. In addition, the BBR/TRAIL combination treatment ... |
|
|
Synthetic double-stranded RNA induces interleukin-32 in bronchial epithelial cells.
Exp. Lung Res. 41 , 335-43, (2015) Interleukin (IL)-32 is a novel cytokine and is involved in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases, including asthma and COPD. However, the regulatory mechanisms of IL-32 expression and its precise pathogenic role remain to be defined. Given that vi... |
|
|
Blockade of TGF-β-activated kinase 1 prevents advanced glycation end products-induced inflammatory response in macrophages.
Cytokine 78 , 62-8, (2015) Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), inflammatory-activated macrophages are essential in the initiation and progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN). TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) plays a vital role in innate immune responses and inflammation. However, l... |
|
|
The anti-inflammatory drug BAY 11-7082 suppresses the MyD88-dependent signalling network by targeting the ubiquitin system.
Biochem. J. 451 , 427-37, (2013) The compound BAY 11-7082 inhibits IκBα [inhibitor of NF-κB (nuclear factor κB)α] phosphorylation in cells and has been used to implicate the canonical IKKs (IκB kinases) and NF-κB in >350 publications. In the present study we report that BAY 11-7082 does not ... |