| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
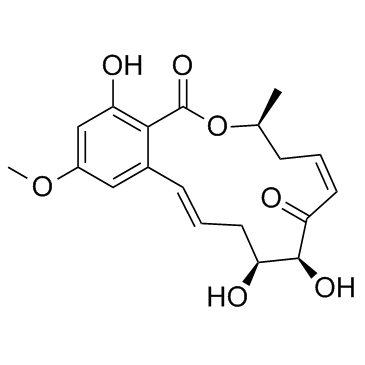 |
5Z-7-Oxozeaenol
CAS:253863-19-3 |
|
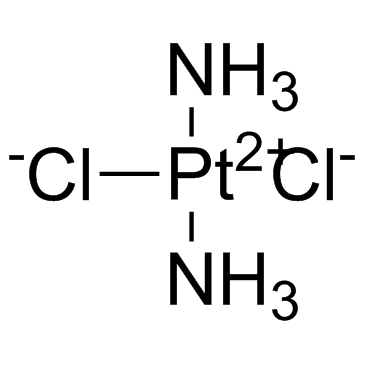 |
Cisplatin
CAS:15663-27-1 |
|
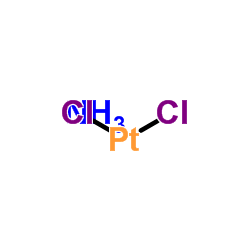 |
trans-Dichlorodiamineplatinum(II)
CAS:14913-33-8 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |