Fomepizole
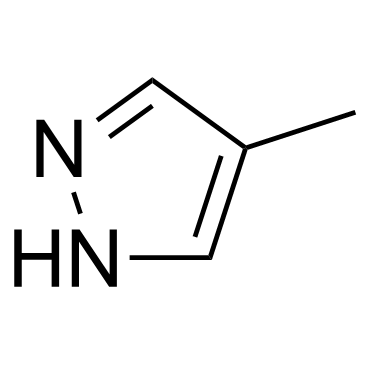
Fomepizole structure
|
Common Name | Fomepizole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7554-65-6 | Molecular Weight | 82.104 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 243.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6N2 | Melting Point | 13°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 96.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Schisandrol B protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibition of CYP-mediated bioactivation and regulation of liver regeneration.
Toxicol. Sci. 143(1) , 107-15, (2014) Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is the most frequent cause of drug-induced acute liver failure. Schisandra sphenanthera is a traditional hepato-protective Chinese medicine and Schisandrol B (SolB) is one of its major active constituents. In this study, the prot... |
|
|
Metabolic characterization of meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid in liver microsomes and in mice.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 76 , 94-102, (2015) meso-Dihydroguaiaretic acid (MDGA) is a major component of Myristica fragrans and Machilus thunbergii that is traditionally used as a spice and for medicinal purposes. Despite reports of various biological activities exerted by MDGA, there is no information r... |
|
|
Induction of CYP26A1 by metabolites of retinoic acid: evidence that CYP26A1 is an important enzyme in the elimination of active retinoids.
Mol. Pharmacol. 87(3) , 430-41, (2015) All-trans-retinoic acid (atRA), the active metabolite of vitamin A, induces gene transcription via binding to nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs). The primary hydroxylated metabolites formed from atRA by CYP26A1, and the subsequent metabolite 4-oxo-atRA, b... |
|
|
Czech mass methanol outbreak 2012: epidemiology, challenges and clinical features.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 52(10) , 1013-24, (2014) Methanol poisonings occur frequently globally, but reports of larger outbreaks where complete clinical and laboratory data are reported remain scarce. The objective of the present study was to report the data from the mass methanol poisoning in the Czech Repu... |
|
|
Locally-generated acetaldehyde is involved in ethanol-mediated LTP inhibition in the hippocampus.
Neurosci. Lett. 537 , 40-3, (2013) Consistent with the ability of severe alcohol intoxication to impair memory, high concentrations of ethanol (60mM) acutely inhibit long-term potentiation (LTP) in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. To account for this, we hypothesized that local metabo... |
|
|
Ethanol at low concentrations protects glomerular podocytes through alcohol dehydrogenase and 20-HETE.
Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 116-117 , 88-98, (2015) Clinical studies suggest cardiovascular and renal benefits of ingesting small amounts of ethanol. Effects of ethanol, role of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) or of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) in podocytes of the glomerular filtration barrier have no... |
|
|
Downregulation of Gabra4 expression during alcohol withdrawal is mediated by specific microRNAs in cultured mouse cortical neurons.
Brain Behav. 5 , e00355, (2015) Alcohol abuse and dependence are a serious public health problem. A large number of alcohol-regulated genes, (ARGs) are known to be influenced by alcohol use and withdrawal (AW), and recent evidence suggests that neuroadaptation to alcohol may be due in part ... |
|
|
Systematic and Molecular Basis of the Antibacterial Action of Quinoxaline 1,4-Di-N-Oxides against Escherichia coli.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0136450, (2015) Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides (QdNOs) are widely known as potent antibacterial agents, but their antibacterial mechanisms are incompletely understood. In this study, the transcriptomic and proteomic profiles of Escherichia coli exposed to QdNOs were integrative... |