N-Phenylanthranilic acid
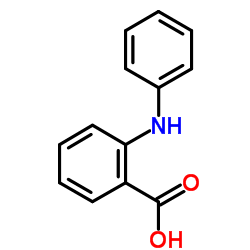
N-Phenylanthranilic acid structure
|
Common Name | N-Phenylanthranilic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91-40-7 | Molecular Weight | 213.232 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 385.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H11NO2 | Melting Point | 182-185 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 186.7±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted approach for identifying chemicals with potential safety proble... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Protein biomarkers of nephrotoxicity; a review and findings with cyclosporin A, a signal transduction kinase inhibitor and N-phenylanthranilic acid.
Cancer Biomark. 1(1) , 59-67, (2005) Biomarkers of nephrotoxicity range from plasma and urine biochemistry, enzymic assays for brush border and lysosomal markers plus new protein markers by immunoassay. Because of the complexity of the nephron and regional sensitivity to xenobiotics, it is impor... |
|
|
QSAR study on permeability of hydrophobic compounds with artificial membranes.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 3756-67, (2007) We previously reported a classical quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) equation for permeability coefficients (P(app-pampa)) by parallel artificial membrane permeation assay (PAMPA) of structurally diverse compounds with simple physicochemical... |
|
|
5-Carboxyfluorescein tagged N-phenylanthranilamide as a tracer reagent for fluorescence polarization: a robust method to screen MAPK pathway allosteric inhibitors.
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 46(12) , 2043-5, (2010) Fluorescence polarization using N(alpha)-(fluorescein-5-carbonyl)-N(epsilon)-(N-[2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl]-3,4-difluoroanthraniloyl)lysyl amide is capable of rapidly identifying inhibitor ligands that bind to an allosteric site in MEK1. |
|
|
Discovery of substituted 3-(phenylamino)benzoic acids as potent and selective inhibitors of type 5 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C3).
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 1464-8, (2011) Aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) also known as type 5 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase has been implicated as one of the key enzymes driving the elevated intratumoral androgen levels observed in castrate resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). AKR1C3 inhibition the... |
|
|
Stimulating effects of dopamine on chloride transport across the rat caudal epididymal epithelium in culture.
Biol. Reprod. 80(1) , 13-23, (2009) The present study investigated the effects of dopamine on chloride transport across cultured rat caudal epididymal epithelium. The results showed that dopamine induced a biphasic short-circuit current (Isc) in a concentration-dependent manner. The dopamine-in... |
|
|
Cellular mechanism underlying formaldehyde-stimulated Cl- secretion in rat airway epithelium.
PLoS ONE 8(1) , e54494, (2013) Recent studies suggest that formaldehyde (FA) could be synthesized endogeneously and transient receptor potential (TRP) channel might be the sensor of FA. However, the physiological significance is still unclear.The present study investigated the FA induced e... |
|
|
A synthetic chloride channel restores chloride conductance in human cystic fibrosis epithelial cells.
PLoS ONE 7(4) , e34694, (2012) Mutations in the gene-encoding cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) cause defective transepithelial transport of chloride (Cl(-)) ions and fluid, thereby becoming responsible for the onset of cystic fibrosis (CF). One strategy to reduce ... |