Ubiquinone Q0
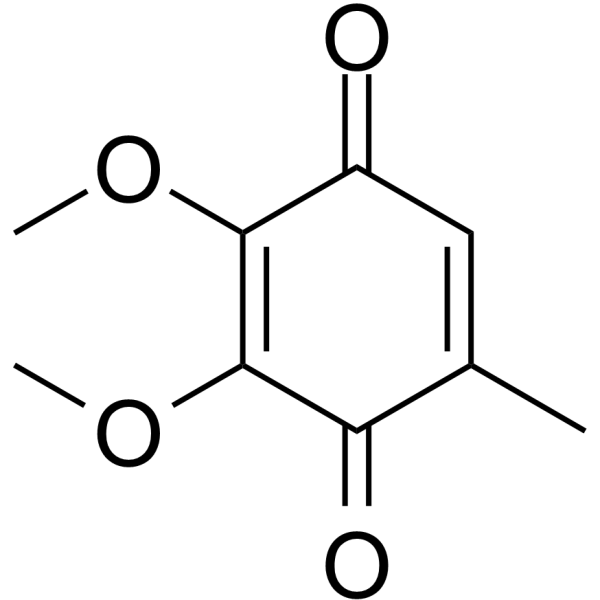
Ubiquinone Q0 structure
|
Common Name | Ubiquinone Q0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 605-94-7 | Molecular Weight | 182.173 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 331.4±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O4 | Melting Point | 58-60 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 148.6±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cofactor Specificity of the Bifunctional Alcohol and Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (AdhE) in Wild-Type and Mutant Clostridium thermocellum and Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum.
J. Bacteriol. 197 , 2610-9, (2015) Clostridium thermocellum and Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum are thermophilic bacteria that have been engineered to produce ethanol from the cellulose and hemicellulose fractions of biomass, respectively. Although engineered strains of T. saccharolyticu... |
|
|
Prerequisites for ubiquinone analogs to prevent mitochondrial permeability transition-induced cell death.
J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 44(1) , 207-12, (2012) The permeability transition pore (PTP) is a mitochondrial inner membrane channel involved in cell death. The inhibition of PTP opening has been proved to be an effective strategy to prevent cell death induced by oxidative stress. Several ubiquinone analogs ar... |
|
|
Ubiquinone analogs: a mitochondrial permeability transition pore-dependent pathway to selective cell death.
PLoS ONE 5 , e11792, (2010) Prolonged opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) leads to cell death. Various ubiquinone analogs have been shown to regulate PTP opening but the outcome of PTP regulation by ubiquinone analogs on cell fate has not been studied yet.The... |
|
|
Immunochemical identification of coenzyme Q0-dihydrolipoamide adducts in the E2 components of the alpha-ketoglutarate and pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes partially explains the cellular toxicity of coenzyme Q0.
J. Biol. Chem. 279 , 27278-27285, (2004) Coenzyme Q(0) (Q(0)), a strong electrophile, is toxic to insulin-producing cells. Q(0) was incubated with rat and human pancreatic islets and INS-1 insulinoma cells, and its attachment to cellular proteins was studied with Western analysis using antiserum rai... |
|
|
Photolabile ubiquinone analogues for identification and characterization of quinone binding sites in proteins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 3457-66, (2010) Novel azidoquinone for direct photolabeling of quinone binding sites in proteins. |
|
|
Sonochemistry of quinones in argon-saturated aqueous solutions: enhanced cytochrome c reduction.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 12(9) , 850-4, (1999) Sonolysis of argon-saturated aqueous quinone solutions resulted in an enhancement in ferricytochrome c (Cyt c) reduction. Upon addition of superoxide dismutase, Cyt c reduction was partially inhibited, thus implying a role of superoxide ion in this reduction ... |
|
|
Site-specific binding of quinones to proteins through thiol addition and addition-elimination reactions.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(17) , 6140-1, (2005) Ubiquinone-0, menaquinone-0, and 2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone were site-specifically bound to free cysteine of proteins (yeast iso-1 cytochrome c as a model protein) through thioether bond formation. Model thioether quinone conjugates showed unexpected re... |
|
|
Thiol metabolomics of endothelial cells using capillary liquid chromatography mass spectrometry with isotope coded affinity tags.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1218(18) , 2561-8, (2011) Thiol and disulfide levels are critical to maintaining the redox potential of a cell. Perturbations of these levels are important in disease pathogenesis. To improve endogenous mammalian metabolome quantitation, thiol specific tagging, extraction and relative... |
|
|
Ubiquinone-0 (2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone) as effective catalyzer of ascorbate and epinephrine oxidation and damager of neuroblastoma cells.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 55(1) , 85-91, (1998) The kinetics of ascorbate (AscH ) and epinephrine (EP) oxidation in the presence of 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone (UQ) were studied in 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, at 37 degrees C by using a Clark electrode and ESR techniques. UQ at nanomolar co... |
|
|
Quinones facilitate the self-assembly of the phosphorylated tubulin binding region of tau into fibrillar polymers.
Biochemistry 43(10) , 2888-97, (2004) The fragment of tau containing the first and third tubulin-binding motifs, involved in self-assembly of tau, was phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA). In the presence of hydroxynonenal (HNE) or in the presence of quinones such as juglone, 2,3-dimethoxy-5-... |