MPP+ iodide
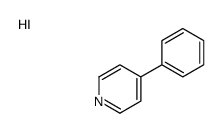
MPP+ iodide structure
|
Common Name | MPP+ iodide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 36913-39-0 | Molecular Weight | 283.10800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H10IN | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
A new dopaminergic nigro-olfactory projection.
Acta Neuropathol. 130 , 333-48, (2015) Parkinson disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by massive loss of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Whereas onset of motor impairments reflects a rather advanced stage of the disorder, hyposmia often marks the beginning of the disease. Litt... |
|
|
The contribution of human OCT1, OCT3, and CYP3A4 to nitidine chloride-induced hepatocellular toxicity.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(7) , 1227-34, (2014) Nitidine chloride (NC), a quaternary ammonium alkaloid, has numerous pharmacological effects, such as anticancer activity. However, it was found that NC also has hepatocellular toxicity. Because organic cation transporters 1 and 3 (OCT1 and OCT3) might mediat... |
|
|
Nucleoside transporters and human organic cation transporter 1 determine the cellular handling of DNA-methyltransferase inhibitors.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 171(16) , 3868-80, (2014) Inhibitors of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), such as azacytidine, decitabine and zebularine, are used for the epigenetic treatment of cancer. Their action may depend upon their translocation across the plasma membrane. The aim of this study was to identify t... |
|
|
Vesicular monoamine transporter substrate/inhibitor activity of MPTP/MPP+ derivatives: a structure-activity study.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 760-8, (2008) The active metabolite of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), N-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+)), selectively destroys the dopaminergic neurons and induces the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Inhibition of mitochondrial complex I and/or the... |
|
|
MDR1 transporter protects against paraquat-induced toxicity in human and mouse proximal tubule cells.
Toxicol. Sci. 141(2) , 475-83, (2014) Paraquat is a herbicide that is highly toxic to the lungs and kidneys following acute exposures. Prior studies have demonstrated that the organic cation transporter 2 and multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 1 contribute to the urinary secretion of paraquat ... |
|
|
Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine by monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
Nature 311 , 467-469, (1984) 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) causes degeneration of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway in several animal species, including humans, monkeys and mice. Changes observed after MPTP administration include marked decrements in the neostr... |
|
|
Secreted miR-34a in astrocytic shedding vesicles enhanced the vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons to neurotoxins by targeting Bcl-2.
Protein Cell. 6 , 529-40, (2015) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of noncoding RNAs that regulates target gene expression at posttranscriptional level, leading to further biological functions. We have demonstrated that microvesicles (MVs) can deliver miRNAs into target cells as a novel way of ... |
|
|
Ethyl-eicosapentaenoate modulates changes in neurochemistry and brain lipids induced by parkinsonian neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium in mouse brain slices
Eur. J. Oral Sci. 649 , 127-34, (2010) Evidence suggests a link between Parkinson's disease and the dietary intake of omega (n)−3 and n−6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Presently, we investigated whether an acute dose of parkinsonian neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP +) affects bra... |
|
|
In Vitro Metabolic Pathways of the New Anti-Diabetic Drug Evogliptin in Human Liver Preparations.
Molecules 20 , 21802-15, (2015) Evogliptin ((R)-4-((R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoyl)-3-(tert-butoxymethyl)-piperazin-2-one), is a new dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor used for the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus. The in vitro metabolic pathways of evogliptin were identi... |
|
|
Metabolism of the neurotoxic tertiary amine, MPTP, by brain monoamine oxidase.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 120 , 574, (1984) The neurotoxic chemical MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,4,5-tetrahydropyridine) is metabolized by rat brain mitochondrial fractions at a rate of 0.91 +/- 0.02 nmoles/mg protein/min. The major metabolite has been identified as the 1-methyl-4- phenylpyridinium spec... |