L-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine
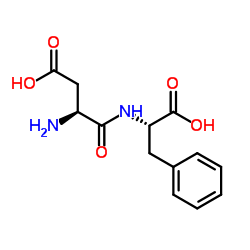
L-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine structure
|
Common Name | L-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13433-09-5 | Molecular Weight | 280.276 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 528.4±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16N2O5 | Melting Point | 236-239ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 273.4±32.9 °C | |
|
Lanthanide ion-mediated peptide hydrolysis.
Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 38 , 25-41, (2001)
|
|
|
pH-dependence of complexion constants and complex mobility in capillary electrophoresis separations of dipeptide enantiomers.
Electrophoresis 22(15) , 3163-70, (2001) The chiral separation of the LL- and DD-enantiomers of the dipeptides Ala-Tyr, Phe-Phe, and Asp-PheOMe has been investigated at pH 2.5 and pH 3.5 using beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD), heptakis-(2,6-di-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin, and heptakis-(2,3,6-tri-O-methyl... |
|
|
[Determination of aspartame--methyl ester of L-aspartyl-L-phenyl- alanine using the amino acid analyzer].
Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 23(3) , 426-8, (1987) A technique for quantitative determining of the synthetic sweetener aspartame. NH2-Asp-Phe-OMe and its hydrolysis product, NH2-Asp-Phe-OH, is proposed based on the use of an amino acid analyzer. |
|
|
Solid state stability studies of model dipeptides: aspartame and aspartylphenylalanine.
J. Pharm. Sci. 86(1) , 64-71, (1997) Some solid-state pharmaceutical properties and the solid-state thermal stability of the model dipeptides aspartame (APM) and aspartylphenylalanine (AP), have been investigated. Studies by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermal gravimetric analysis (... |
|
|
Structure of a 1:1 complex between L-Asp-L-Phe and L-His-Gly.
Acta Crystallogr. C 49 ( Pt 9) , 1673-6, (1993) Both molecules occur in slightly folded conformations, characterized by phi 2 = -93.7 degrees in L-His-Gly and an unusual phi 2 = 60.2 degrees in L-Asp-L-Phe. The peptide linkage of L-His-Gly displays a substantial deviation from planarity with omega 1 = -163... |
|
|
Intestinal absorption of aspartame decomposition products in adult rats.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 40(12) , 1337-45, (1991) The dipeptide sweetener aspartame (N-L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine, 1-methyl ester; alpha-APM) is relatively stable in dry powder form. However, when exposed to elevated temperature, extremes of pH and/or moisture, alpha-APM is converted into a variety of ... |
|
|
Intestinal hydrolysis of aspartylphenylalanine--the metabolic product of aspartame.
Gastroenterology 91(4) , 931-7, (1986) Aspartame [Nutrasweet, Equal (Searle Consumer Products, Chicago, Ill.)] is the methyl ester of the dipeptide aspartylphenylalanine (Asp-Phe). After hydrolysis of the ester bond in the intestinal lumen, the dipeptide is apparently absorbed and digested in the ... |
|
|
Identification of N-beta-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine as a normal constituent of human plasma and urine.
J. Nutr. 119(5) , 713-21, (1989) A new beta-aspartyl dipeptide, N-beta-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine (beta-AP), has been isolated and identified in urine and plasma from normal human volunteers. beta-AP was isolated from urine samples by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Its identi... |
|
|
Thermodynamic determination of the binding constants of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors by a displacement method.
FEBS Lett. 581(18) , 3449-54, (2007) Somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme (s-ACE) plays a central role in blood pressure regulation and has been the target of most antihypertensive drugs. A displacement isothermal titration calorimetry method has been used to accurately determine the binding ... |
|
|
Structural studies of C-amidated amino acids and peptides: crystal structures of Z-Gly-Phe-NH2, Tyr-Lys-NH2, and Asp-Phe-NH2.
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 48(3) , 374-81, (2000) As part of the series investigating the structural features of C-terminal amidated amino acids and peptides, three crystal structures of Z-Gly-Phe-NH2, Tyr-Lys-NH2, and Asp-Phe-NH2 were analyzed by the X-ray diffraction method, and their molecular conformatio... |