Solid state stability studies of model dipeptides: aspartame and aspartylphenylalanine.
S S Leung, D J Grant
Index: J. Pharm. Sci. 86(1) , 64-71, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Some solid-state pharmaceutical properties and the solid-state thermal stability of the model dipeptides aspartame (APM) and aspartylphenylalanine (AP), have been investigated. Studies by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), high-performance liquid chromatography, powder X-ray diffraction, and optical microscopy have shown that the dipeptides undergo solid state intramolecular aminolysis of the type, solid --> solid + gas. This reaction was observed for APM at 167-180 degrees C with the liberation of methanol and for AP at 186-202 degrees C with the liberation of water. The exclusive solid product of the degradation reaction of both dipeptides is the cyclic compound 3-(carboxymethyl)-6-benzyl-2,5-dioxopiperazine. The rates of the degradation reactions were monitored by isothermal TGA and by temperature-ramp DSC and were found to follow kinetics based on nucleation control with activation energies of about 266 kJ mol(-1) for APM and 234 kJ mol(-1) for AP.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
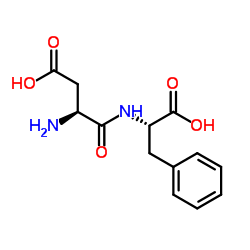 |
L-Aspartyl-L-phenylalanine
CAS:13433-09-5 |
C13H16N2O5 |
|
Lanthanide ion-mediated peptide hydrolysis.
2001-01-01 [Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 38 , 25-41, (2001)] |
|
pH-dependence of complexion constants and complex mobility i...
2001-09-01 [Electrophoresis 22(15) , 3163-70, (2001)] |
|
[Determination of aspartame--methyl ester of L-aspartyl-L-ph...
1987-01-01 [Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 23(3) , 426-8, (1987)] |
|
Structure of a 1:1 complex between L-Asp-L-Phe and L-His-Gly...
1993-09-15 [Acta Crystallogr. C 49 ( Pt 9) , 1673-6, (1993)] |
|
Intestinal absorption of aspartame decomposition products in...
1991-12-01 [Metab. Clin. Exp. 40(12) , 1337-45, (1991)] |