Gramicidin A
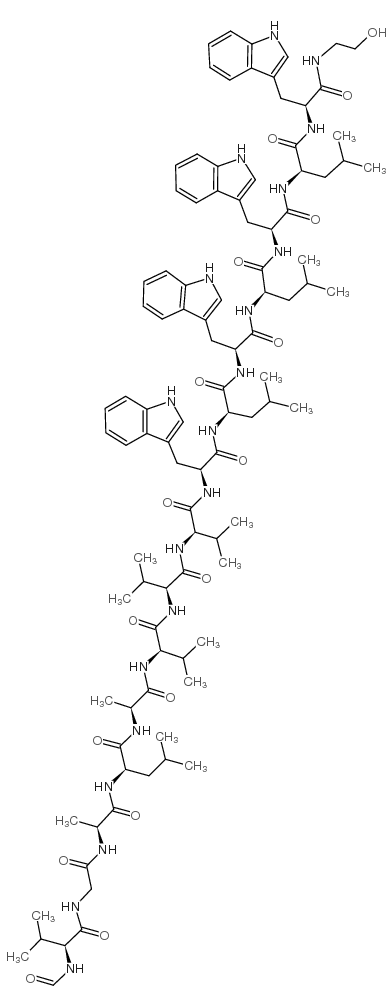
Gramicidin A structure
|
Common Name | Gramicidin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 11029-61-1 | Molecular Weight | 1882.29000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C99H140N20O17 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Unsaturated lipids protect the integral membrane peptide gramicidin A from singlet oxygen
FEBS Lett. 588(9) , 1590-5, (2014) • Unsaturated lipids protect gramicidin channels from photosensitized inactivation. • Photosensitizer binding to membrane is independent of lipid unsaturation. • Double bonds in lipids reduce gramicidin inactivation by tert-butyl hydroperoxide. |
|
|
Importance of indole N-H hydrogen bonding in the organization and dynamics of gramicidin channels.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1838(1 Pt B) , 419-28, (2014) The linear ion channel peptide gramicidin represents an excellent model for exploring the principles underlying membrane protein structure and function, especially with respect to tryptophan residues. The tryptophan residues in gramicidin channels are crucial... |
|
|
Tonic GABAA conductance bidirectionally controls interneuron firing pattern and synchronization in the CA3 hippocampal network.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(1) , 504-9, (2014) The spiking output of interneurons is key for rhythm generation in the brain. However, what controls interneuronal firing remains incompletely understood. Here we combine dynamic clamp experiments with neural network simulations to understand how tonic GABAA ... |
|
|
Inversion of membrane surface charge by trivalent cations probed with a cation-selective channel.
Langmuir 28(45) , 15824-30, (2012) We demonstrate that the cation-selective channel formed by gramicidin A can be used as a reliable sensor for studying the multivalent ion accumulation at the surfaces of charged lipid membranes and the "charge inversion" phenomenon. In asymmetrically charged ... |
|
|
N-terminally glutamate-substituted analogue of gramicidin A as protonophore and selective mitochondrial uncoupler.
PLoS ONE 7(7) , e41919, (2012) Limited uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation could be beneficial for cells by preventing excessive generation of reactive oxygen species. Typical uncouplers are weak organic acids capable of permeating across membranes with a narrow gap between efficacy an... |
|
|
The association between exit site infection and subsequent peritonitis among peritoneal dialysis patients.
Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 7(8) , 1266-71, (2012) Peritonitis is the most common infectious complication seen in peritoneal dialysis (PD). Traditionally, exit site infection (ESI) has been thought to predispose PD patients to peritonitis, although the risks have not been quantified. This study aimed to quant... |
|
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of gramicidin S-inspired cyclic mixed α/β-peptides.
Chem. Biodivers. 9(11) , 2494-506, (2012) Via a Mannich reaction involving a dibenzyliminium species and the titanium enolates of Evans' chiral acylated oxazolidinones the β(2)-amino acids (R)- and (S)-Fmoc-β(2)homovaline and (R)-Fmoc-β(2)homoleucine are synthesized. These building blocks were used, ... |
|
|
Human AQP1 is a constitutively open channel that closes by a membrane-tension-mediated mechanism.
Biophys. J. 104(1) , 85-95, (2013) This work presents experimental results combined with model-dependent predictions regarding the osmotic-permeability regulation of human aquaporin 1 (hAQP1) expressed in Xenopus oocyte membranes. Membrane elastic properties were studied under fully controlled... |
|
|
Cyclic decapeptide gramicidin S derivatives containing phosphines: novel ligands for asymmetric catalysis.
Dalton Trans. 42(6) , 1973-8, (2013) The cyclic peptide gramicidin S was used as a rigid template to provide novel peptide-based bisphosphine ligands for transition metal catalysis. Two bisphosphine-coordinated Rh(I) complexes allowed asymmetric hydrogenation with 10-52% ee and the corresponding... |
|
|
The determinants of hydrophobic mismatch response for transmembrane helices.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1828(2) , 851-63, (2013) Hydrophobic mismatch arises from a difference in the hydrophobic thickness of a lipid membrane and a transmembrane protein segment, and is thought to play an important role in the folding, stability and function of membrane proteins. We have investigated the ... |