lead diacetate trihydrate
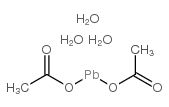
lead diacetate trihydrate structure
|
Common Name | lead diacetate trihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6080-56-4 | Molecular Weight | 379.33400 | |
| Density | 2,55 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 280°C | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H12O7Pb | Melting Point | 75 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 40ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Preventive efficacy of bulk and nanocurcumin against lead-induced oxidative stress in mice.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 152(1) , 31-40, (2013) Chronic lead exposure is associated with several health disorders in humans and animals. Lead exposure leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species and depletes body antioxidant enzymes causing damage to various macromolecules and ultimately cell death.... |
|
|
Plasmacatalytic removal of lead acetate assisted by precipitation.
Chemosphere 107 , 304-10, (2014) The Gliding Arc Discharge (GAD) is an efficient non-thermal plasma technique able to degrade organic compounds dispersed in water at atmospheric pressure. The degradation of the organometallic lead acetate (PbAc) in aqueous solution was performed by two disti... |
|
|
Nephroprotective effect of calcium channel blockers against toxicity of lead exposure in mice.
Toxicol. Lett. 218(3) , 273-80, (2013) Exposure to lead (Pb) can induce kidney damage, which is related to induction of oxidative damage and disturbance of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Pb can readily permeate through dihydropyridine-sensitive L-type calcium channels and accumulate within cel... |
|
|
Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8661 alleviates lead toxicity in mice.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 150(1-3) , 264-71, (2012) Lead causes a broad range of adverse effects in humans and animals. The objective was to evaluate the potency of lactobacilli to bind lead in vitro and the protective effects of a selected Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8661 against lead-induced toxicity in mice... |
|
|
Involvement of CTR1 and ATP7A in lead (Pb)-induced copper (Cu) accumulation in choroidal epithelial cells.
Toxicol. Lett. 225(1) , 110-8, (2014) The blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCB) plays a key role in maintaining copper (Cu) homeostasis in the brain. Cumulative evidences indicate that lead (Pb) exposure alters cerebral Cu homeostasis, which may underlie the development of neurodegenerative dis... |
|
|
Oxidative stress: a possible mechanism for lead-induced apoptosis and nephrotoxicity.
Toxicol. Mech. Methods 22(9) , 705-10, (2012) Lead-induced nephrotoxicity is a human health hazard problem. In this study, Human mesangial cells (HMCs) were treated with different concentration of lead acetate (5, 10, 20 μmol/l) in order to investigate the oxidative stress and apoptotic changes. It was r... |
|
|
Lead acetate reduces the ability of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to support hematopoiesis in vitro.
Mol. Med. Report. 6(4) , 827-32, (2012) Plumbum (Pb) is a heavy metal toxin that causes many pathophysiological effects in various systems of the human body. It has previously been reported that excessive lead trioxide causes hematopoietic system toxicity. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), as cells wi... |
|
|
Effects of exposure to lead on the peripheral motor system of the rat. An ultrastructural study.
Neurosciences (Riyadh.) 18(1) , 52-7, (2013) To investigate the morphological changes in the peripheral motor system of the rat induced by exposure to lead.This study was conducted at the Anatomy Department, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia from January 201... |
|
|
Bystander effects of PC12 cells treated with Pb²⁺ depend on ROS-mitochondria-dependent apoptotic signaling via gap-junctional intercellular communication.
Toxicol. Lett. 229(1) , 150-7, (2014) The demonstration of bystander effect, which means injured cells propagate damage to neighboring cells, in whole organisms has clear implication of the potential relevance of the non-targeted response to human health. Here we show that 10 μM lead acetate, the... |
|
|
Microglial disruption in young mice with early chronic lead exposure
Toxicol. Lett. 220(1) , 44-52, (2013) • Neuroinflammatory markers and microglia were compared in young mice with and without early chronic Pb exposure. • Mice with Pb levels from 2.66 to 20.31μg/dL had dose-dependent reduction of cytokine IL6. • Mice with Pb levels from 2.66 to 20.31μg/dL had dos... |