Effects of exposure to lead on the peripheral motor system of the rat. An ultrastructural study.
Mohammed H Badawoud, Sherif M Hassan
Index: Neurosciences (Riyadh.) 18(1) , 52-7, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To investigate the morphological changes in the peripheral motor system of the rat induced by exposure to lead.This study was conducted at the Anatomy Department, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia from January 2011 to January 2012. Female adult albino rats (n=10) were given lead acetate in their drinking water (500mg/L) for a period of 30 days. Female adult albino rats (n=5) were used as control. The soleus and gastrocnemius muscles were dissected and processed for electron microscopy.Lead administration induced morphological changes in all constituents of the peripheral motor system of the rat, including; extension of long processes by Schwann cells, engorgement of nerve terminals, withdrawal of some terminals, and muscle fiber alterations.Lead toxicity is detrimental to all constituents of the peripheral motor system of the rat. The histopathological changes explain some of the clinical manifestations of lead toxicity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
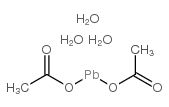 |
lead diacetate trihydrate
CAS:6080-56-4 |
C4H12O7Pb |
|
Preventive efficacy of bulk and nanocurcumin against lead-in...
2013-04-01 [Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 152(1) , 31-40, (2013)] |
|
Plasmacatalytic removal of lead acetate assisted by precipit...
2014-07-01 [Chemosphere 107 , 304-10, (2014)] |
|
Nephroprotective effect of calcium channel blockers against ...
2013-04-26 [Toxicol. Lett. 218(3) , 273-80, (2013)] |
|
Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8661 alleviates lead toxicity in...
2012-12-01 [Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 150(1-3) , 264-71, (2012)] |
|
Involvement of CTR1 and ATP7A in lead (Pb)-induced copper (C...
2014-02-10 [Toxicol. Lett. 225(1) , 110-8, (2014)] |