2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione
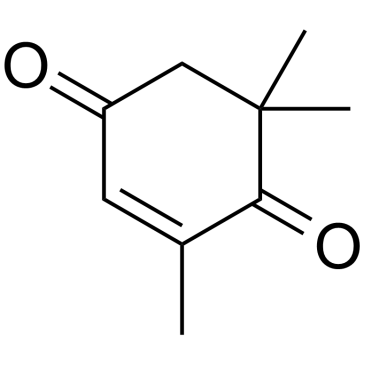
2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione structure
|
Common Name | 2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1125-21-9 | Molecular Weight | 152.190 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 214.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12O2 | Melting Point | 26-28 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 96.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Engineering towards nitroreductase functionality in ene-reductase scaffolds.
ChemBioChem. 16(5) , 811-8, (2015) Nitroreductases (NRs) and ene-reductases (ERs) both utilize flavin mononucleotide cofactors but catalyze distinct reactions. NRs reduce nitroaromatics, whereas ERs reduce unsaturated C=C double bonds, and these functionalities are known to somewhat overlap. R... |
|
|
Bioreduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones and aldehydes by non-conventional yeast (NCY) whole-cells.
Bioresour. Technol. 102(5) , 3993-8, (2011) The bioreduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones (ketoisophorone, 2-methyl- and 3-methyl-cyclopentenone) and aldehydes [(S)-(-)-perillaldehyde and α-methyl-cinnamaldehyde] by 23 "non-conventional" yeasts (NCYs) belonging to 21 species of the genera Candida, Crypto... |
|
|
An engineered old yellow enzyme that enables efficient synthesis of (4R,6R)-Actinol in a one-pot reduction system.
ChemBioChem. 16(3) , 440-5, (2015) (4R,6R)-Actinol can be stereo-selectively synthesized from ketoisophorone by a two-step conversion using a mixture of two enzymes: Candida macedoniensis old yellow enzyme (CmOYE) and Corynebacterium aquaticum (6R)-levodione reductase. However, (4S)-phorenol, ... |
|
|
Old Yellow Enzyme from Candida macedoniensis catalyzes the stereospecific reduction of the C=C bond of ketoisophorone.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66(12) , 2651-7, (2002) Microorganisms were screened for ones that reduced 3,5,5-trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione (ketoisophorone; KIP), and several strains were found to produce (6R)-2,2,6-trimethylcyclohexane-1,4-dione (levodione). The enzyme catalyzing the reduction of the C=C b... |
|
|
Quality and functionality of saffron: quality control, species assortment and affinity of extract and isolated saffron compounds to NMDA and sigma1 (sigma-1) receptors.
Planta Med. 74(7) , 764-72, (2008) Extracts from saffron, the dried stigmata from Crocus sativus L., are being used more and more in preclinical and clinical trials for the treatment of cancer and depression. Because of the known quality problems of saffron, HPLC methods on RP(18) 2.5 microm a... |
|
|
Enoate reductases from non conventional yeasts: bioconversion, cloning, and functional expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
J. Biotechnol. 156(4) , 279-85, (2010) Old yellow enzymes (OYEs, EC 1.6.99.1) are flavin-dependent oxidoreductases that catalyze the stereoselective trans-hydrogenation of the double bond, representing a promising alternative to metal-based catalysis. Bioconversion of ketoisophorone (KIP) by 28 no... |
|
|
Ketoisophorone transformation by Marchantia polymorpha and Nicotiana tabacum cultured cells.
Z. Naturforsch., C, J. Biosci. 63(5-6) , 403-8, (2008) Stereospecific olefin (C=C) and carbonyl (C=O) reduction of the readily available prochiral compound ketoisophorone (2,2,6-trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione) (1) by Marchantia polymorpha and Nicotiana tabacum cell suspension cultures produce the chiral produc... |
|
|
Worldwide market screening of saffron volatile composition. Maggi L, et al.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 89(11) , 1950-54, (2011)
|
|
|
Description of volatile compounds generated by the degradation of carotenoids in paprika, tomato and marigold oleoresins. Rios JJ, et al.
Food Chem. 106(3) , 1145-53, (2008)
|