2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione
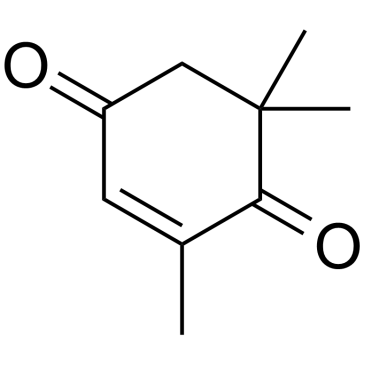
2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione structure
|
Common Name | 2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1125-21-9 | Molecular Weight | 152.190 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 214.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12O2 | Melting Point | 26-28 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 96.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dioneKetoisophorone (4-Oxoisophorone) is a key intermediate in the synthesis of carotenoids and flavouring agents. Ketoisophorone is an industrially important cyclic endione[1]. |
| Name | 2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ketoisophorone (4-Oxoisophorone) is a key intermediate in the synthesis of carotenoids and flavouring agents. Ketoisophorone is an industrially important cyclic endione[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 214.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 26-28 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.190 |
| Flash Point | 96.1±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 152.083725 |
| PSA | 34.14000 |
| LogP | 0.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.469 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29142900 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2914299000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2914299000. other cyclanic, cyclenic or cyclotherpenic ketones without other oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Engineering towards nitroreductase functionality in ene-reductase scaffolds.
ChemBioChem. 16(5) , 811-8, (2015) Nitroreductases (NRs) and ene-reductases (ERs) both utilize flavin mononucleotide cofactors but catalyze distinct reactions. NRs reduce nitroaromatics, whereas ERs reduce unsaturated C=C double bonds,... |
|
|
Bioreduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones and aldehydes by non-conventional yeast (NCY) whole-cells.
Bioresour. Technol. 102(5) , 3993-8, (2011) The bioreduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones (ketoisophorone, 2-methyl- and 3-methyl-cyclopentenone) and aldehydes [(S)-(-)-perillaldehyde and α-methyl-cinnamaldehyde] by 23 "non-conventional" yeasts (... |
|
|
An engineered old yellow enzyme that enables efficient synthesis of (4R,6R)-Actinol in a one-pot reduction system.
ChemBioChem. 16(3) , 440-5, (2015) (4R,6R)-Actinol can be stereo-selectively synthesized from ketoisophorone by a two-step conversion using a mixture of two enzymes: Candida macedoniensis old yellow enzyme (CmOYE) and Corynebacterium a... |
| 2-Cyclohexene-1,4-dione, 2,6,6-trimethyl- |
| 2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexen-1,4-dione |
| 4-Oxoisophorone,Ketoisophorone |
| EINECS 214-406-2 |
| 2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-2-ene-1,4-dione |
| MFCD00043119 |
| 4-Oxoisophorone |
| 4-Ketoisophorone |
| 2,6,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1,4-dione |
 CAS#:471-01-2
CAS#:471-01-2 CAS#:78-59-1
CAS#:78-59-1 CAS#:518316-69-3
CAS#:518316-69-3 CAS#:127-41-3
CAS#:127-41-3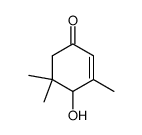 CAS#:14203-59-9
CAS#:14203-59-9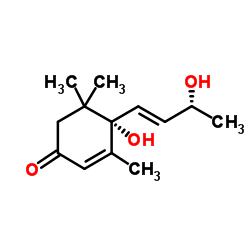 CAS#:23526-45-6
CAS#:23526-45-6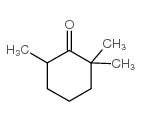 CAS#:2408-37-9
CAS#:2408-37-9![7,9,9-trimethyl-1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-6-en-8-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/122/14203-64-6.png) CAS#:14203-64-6
CAS#:14203-64-6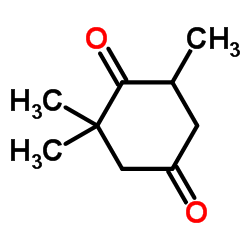 CAS#:20547-99-3
CAS#:20547-99-3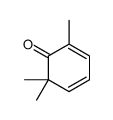 CAS#:13487-30-4
CAS#:13487-30-4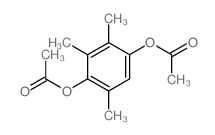 CAS#:7479-28-9
CAS#:7479-28-9
