6-FLUOROMEVALONATE
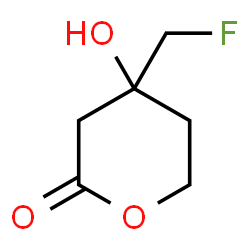
6-FLUOROMEVALONATE structure
|
Common Name | 6-FLUOROMEVALONATE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2822-77-7 | Molecular Weight | 148.132 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 307.8±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9FO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 140.0±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
[Pharmacological control of biosynthesis pathway of mevalonate: effect on the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells].
C. R. Seances. Soc. Biol. Fil. 191(2) , 169-94, (1997) The role of mevalonic acid (MVA) and its products (isoprenoids) in cell proliferation prompted us to investigate the effect of drugs affecting diverse enzymatic steps of the MVA pathway on rat aorta smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation. Competitive inhibito... |
|
|
Effect of lovastatin and fluoromevalonate on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity stimulated with PDGF.
Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. Suppl. 22(1) , S318-20, (1995) 1. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) appears to have a crucial role in cellular proliferation induced by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). However, the mode of activation of the enzyme has been unclear so far. In the present study, we investigated the... |
|
|
Inhibition of the isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway; detection of intermediates by UPLC-MS/MS.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1811(4) , 227-33, (2011) The isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway provides the cell with a variety of compounds which are involved in multiple cellular processes. Inhibition of this pathway with statins and bisphosphonates is widely applied in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and met... |
|
|
Proliferative effect of mevalonate metabolites other than isoprenoids on cultured vascular smooth muscle cells.
Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 20(7-8) , 509-14, (1993) 1. Recent investigations revealed that isoprenoid compounds serve as key substances for cellular proliferation through post-translational modification. Previously we reported that tissues of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) had a lower activity of isopre... |
|
|
Suppression of the proliferation of Ras-transformed cells by fluoromevalonate, an inhibitor of mevalonate metabolism.
Cancer Res. 55(8) , 1732-40, (1995) Mevalonate is the precursor of a number of different products potentially required for the growth of cells, including the prenylated oncoprotein Ras. To determine whether inhibition of mevalonate metabolism would selectively block proliferation of Ras-transfo... |
|
|
Inhibition by 6-fluoromevalonate demonstrates that mevalonate or one of the mevalonate phosphates is necessary for lymphocyte proliferation.
J. Biol. Chem. 265(30) , 18568-75, (1990) The sterol synthesis inhibitor 6-fluoromevalonate (Fmev) was used to explore the role of mevalonate products in lymphocyte proliferation. Fmev blocks the synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and all more distal products in the sterol pathway. When cells wer... |
|
|
Mechanism of the inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis by 6-fluoromevalonate.
Biochem. J. 227(1) , 247-54, (1985) 6-Fluoromevalonate blocks the incorporation of mevalonic acid, but not that of isopentenyl pyrophosphate, into non-saponifiable lipids in a rat liver multienzyme system. With 3H-labelled 6-fluoromevalonate, it was found that 6-fluoromevalonate is converted to... |
|
|
Negative regulation of cell proliferation by mevalonate or one of the mevalonate phosphates.
J. Biol. Chem. 266(27) , 17966-71, (1991) The role of mevalonate and its products in the regulation of cellular proliferation was examined using 6-fluoromevalonate (Fmev), a compound that blocks the conversion of mevalonate pyrophosphate to isopentenyl pyrophosphate. Fmev suppressed DNA synthesis by ... |
|
|
Cantharidin biosynthesis in a blister beetle: inhibition by 6-fluoromevalonate causes chemical disarmament.
Experientia 42(7) , 853-4, (1986) Biosynthesis of cantharidin in a blister beetle, Lytta polita, is effectively inhibited by 6-fluoromevalonate. Inhibition is attributed specifically to the fluorine substituent. Biochemical inhibition has not been demonstrated previously for an arthropod's de... |
|
|
Regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis by intermediates of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 225(1) , 173-9, (1996) The biosynthesis of cholesterol and fatty acid (FA) proceeds by independent pathways. Information is lacking on potential interaction that could provide feedback regulation between these pathways. In an attempt to search for a new approach to produce a dual e... |