Protease K
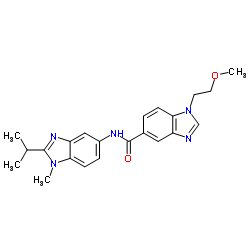
Protease K structure
|
Common Name | Protease K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39450-01-6 | Molecular Weight | 391.466 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H25N5O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Denervation impairs regeneration of amputated zebrafish fins.
BMC Dev. Biol. 14(1) , 49, (2015) Zebrafish are able to regenerate many of its tissues and organs after damage. In amphibians this process is regulated by nerve fibres present at the site of injury, which have been proposed to release factors into the amputated limbs/fins, promoting and susta... |
|
|
Molecular typing of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli colonies originating from outbreaks of E. coli peritonitis syndrome in chicken flocks.
Avian Pathol. 43(4) , 345-56, (2014) Escherichia coli colonies isolated from the bone marrow of fresh dead hens of laying flocks with the E. coli peritonitis syndrome (EPS) were genotyped using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Typing is important from an epidemiological point of view and... |
|
|
Conditioned medium as a strategy for human stem cells chondrogenic differentiation.
J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9 , 714-23, (2015) Paracrine signalling from chondrocytes has been reported to increase the synthesis and expression of cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) by stem cells. The use of conditioned medium obtained from chondrocytes for stimulating stem cells chondrogenic different... |
|
|
Dosage Compensation of X-Linked Muller Element F Genes but Not X-Linked Transgenes in the Australian Sheep Blowfly.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0141544, (2015) In most animals that have X and Y sex chromosomes, chromosome-wide mechanisms are used to balance X-linked gene expression in males and females. In the fly Drosophila melanogaster, the dosage compensation mechanism also generally extends to X-linked transgene... |
|
|
Immediate chromatin immunoprecipitation and on-bead quantitative PCR analysis: a versatile and rapid ChIP procedure.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43 , e38, (2015) Genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) studies have brought significant insight into the genomic localization of chromatin-associated proteins and histone modifications. The large amount of data generated by these analyses, however, require approach... |
|
|
Export-deficient monoubiquitinated PEX5 triggers peroxisome removal in SV40 large T antigen-transformed mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
Autophagy 11 , 1326-40, (2015) Peroxisomes are ubiquitous cell organelles essential for human health. To maintain a healthy cellular environment, dysfunctional and superfluous peroxisomes need to be selectively removed. Although emerging evidence suggests that peroxisomes are mainly degrad... |
|
|
A new CRB1 rat mutation links Müller glial cells to retinal telangiectasia.
J. Neurosci. 35(15) , 6093-106, (2015) We have identified and characterized a spontaneous Brown Norway from Janvier rat strain (BN-J) presenting a progressive retinal degeneration associated with early retinal telangiectasia, neuronal alterations, and loss of retinal Müller glial cells resembling ... |
|
|
Venus trap in the mouse embryo reveals distinct molecular dynamics underlying specification of first embryonic lineages.
EMBO Rep. 16 , 1005-21, (2015) Mammalian development begins with the segregation of embryonic and extra-embryonic lineages in the blastocyst. Recent studies revealed cell-to-cell gene expression heterogeneity and dynamic cell rearrangements during mouse blastocyst formation. Thus, mechanis... |
|
|
Design and development of a novel vaccine for protection against Lyme borreliosis.
PLoS ONE 9(11) , e113294, (2014) There is currently no Lyme borreliosis vaccine available for humans, although it has been shown that the disease can be prevented by immunization with an OspA-based vaccine (LYMErix). Outer surface protein A (OspA) is one of the dominant antigens expressed by... |
|
|
Polysaccharide-free nucleic acids and proteins of Abelmoschus esculentus for versatile molecular studies.
Mol. Biol. (Mosk.) 46(4) , 598-604, (2012) Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) is one of the polysaccharide rich crop plants. The polysaccharides interfere with nucleic acids and protein isolation thereby affecting the downstream molecular analysis. So, to understand the molecular systematics of okra, high ... |