Protease K
Protease K structure
|
Common Name | Protease K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39450-01-6 | Molecular Weight | 391.466 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
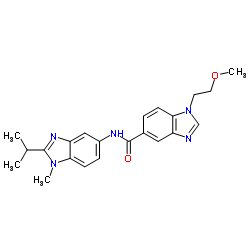
| Molecular Formula | C22H25N5O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Protease KProtease K is a nonspecific serine protease that is useful for general digestion of proteins. Protease K is active in the presence of SDS or urea and over a wide range of pH (4-12), salt concentrations, and temperatures[1]. |
| Name | Proteinase K |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Protease K is a nonspecific serine protease that is useful for general digestion of proteins. Protease K is active in the presence of SDS or urea and over a wide range of pH (4-12), salt concentrations, and temperatures[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H25N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 391.466 |
| Exact Mass | 391.200836 |
| LogP | 2.50 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder | white |
| Index of Refraction | 1.648 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL, slightly hazy, brown-yellow | Miscible with water. |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P284-P304 + P340 + P312-P337 + P313-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38-42 |
| Safety Phrases | 23-24-26-36/37-22-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| HS Code | 35079090 |
|
Denervation impairs regeneration of amputated zebrafish fins.
BMC Dev. Biol. 14(1) , 49, (2015) Zebrafish are able to regenerate many of its tissues and organs after damage. In amphibians this process is regulated by nerve fibres present at the site of injury, which have been proposed to release... |
|
|
Molecular typing of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli colonies originating from outbreaks of E. coli peritonitis syndrome in chicken flocks.
Avian Pathol. 43(4) , 345-56, (2014) Escherichia coli colonies isolated from the bone marrow of fresh dead hens of laying flocks with the E. coli peritonitis syndrome (EPS) were genotyped using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Ty... |
|
|
Conditioned medium as a strategy for human stem cells chondrogenic differentiation.
J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9 , 714-23, (2015) Paracrine signalling from chondrocytes has been reported to increase the synthesis and expression of cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) by stem cells. The use of conditioned medium obtained from cho... |
| Endopeptidase K |
| Tritirachium album proteinase K |
| 1H-Benzimidazole-5-carboxamide, 1-(2-methoxyethyl)-N-[1-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl]- |
| N-(2-Isopropyl-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)-1-(2-methoxyethyl)-1H-benzimidazole-5-carboxamide |
| Prok |

