Probucol
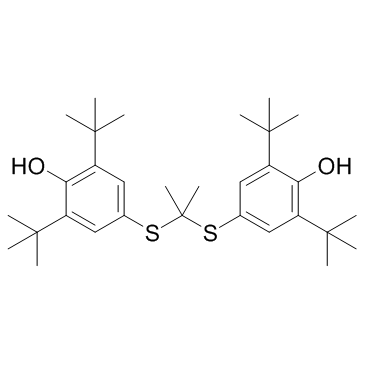
Probucol structure
|
Common Name | Probucol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23288-49-5 | Molecular Weight | 516.842 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 546.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H48O2S2 | Melting Point | 117 118ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 264.9±28.8 °C | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared and assayed 33 coumarin derivatives, and the theoretical pr... |
|
|
Design of more potent squalene synthase inhibitors with multiple activities
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 7402-12, (2010) Antihyperlipidemic morpholine derivatives ( 1– 6), combining several pharmacophore moieties, were evaluated in vitro and in vivo and optimized towards more active SQS inhibitors ( 7– 12). |
|
|
Succinobucol versus probucol: higher efficiency of succinobucol in mitigating 3-NP-induced brain mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in vitro.
Mitochondrion 13(2) , 125-33, (2013) This study evaluated and compared the potential protective effects of probucol and succinobucol, two lipid-lowering compounds with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, on oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by 3-nitropropionic acid... |
|
|
Effects of physicochemical forms of phenazepam and Panavir on their action at ultra-low doses.
Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 153(4) , 455-8, (2012) A concept of physicochemical forms of biologically active substances introduced in investigation of the action mechanism of ultra-low doses allows qualitative explanation of the main effects of ultra-low doses, chemical diversity of biologically active substa... |
|
|
Pharmacological inhibition of coronary restenosis: systemic and local approaches.
Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 15(15) , 2155-71, (2014) Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with stent implantation has revolutionized the treatment of obstructive coronary artery disease. However, the main limitation of this therapy is stent failure, which is usually caused by in-stent restenosis.The aim of ... |
|
|
Nano-pulverization of poorly water soluble compounds with low melting points by a rotation/revolution pulverizer.
Pharmazie 67(8) , 681-6, (2012) We report a method for pulverizing poorly water soluble compounds with low melting points to nanoparticles without producing an amorphous phase using a rotation/revolution pulverizer. Fenofibrate, flurbiprofen, and probucol were used as crystalline model comp... |