Quinoline yellow
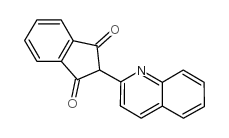
Quinoline yellow structure
|
Common Name | Quinoline yellow | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8003-22-3 | Molecular Weight | 273.28500 | |
| Density | 1.345 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 514.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H11NO2 | Melting Point | 160ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 260ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Self-assembled polymeric nanocarriers for the targeted delivery of retinoic acid to the hair follicle.
Nanoscale 7 , 18651-62, (2015) Acne vulgaris is a highly prevalent dermatological disease of the pilosebaceous unit (PSU). An inability to target drug delivery to the PSU results in poor treatment efficacy and the incidence of local side-effects. Cutaneous application of nanoparticulate sy... |
|
|
Rapid identification of synthetic colorants in food samples by using indium oxide nanoparticle-functionalized porous polymer monolith coupled with HPLC-MS/MS.
Analyst 139(23) , 6168-77, (2014) A synthetic protocol for the preparation of an indium oxide nanoparticle-functionalized poly(methacrylic acid-glycidyl methacrylate-ethylene dimethacrylate-ethanediamine) monolithic column is reported. Various techniques, including scanning electron microscop... |
|
|
The inhalation toxicity of two commercial dyes: solvent yellow 33 and solvent green 3.
Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 8(3) , 358-71, (1987) The quinoline dye 2-(2'-quinolyl)-1,3-indandione or Solvent Yellow 33 (SY) and the anthraquinone dye 1,4-di-p-toluidinoanthraquinone or Solvent Green 3 (SG) are used in many manufactured products including military smoke grenades. During manufacturing, SY or ... |
|
|
Inhalation toxicity of a smoke containing Solvent Yellow 33, Disperse Red 9 and Solvent Green 3 in laboratory animals.
Hum. Toxicol. 3(4) , 289-308, (1984) The repeated-dose inhalation toxicity of a smoke containing a mixture of three dyes was tested in female mice, rats and guinea pigs. The green component dye (Solvent Green 3) was retained in the lungs. Particularly in the rats marked collections of alveolar m... |
|
|
Characterization, purification, and analysis of solvent yellow 33 and solvent green 3 dyes.
J. Chromatogr. A. 391(1) , 219-31, (1987) Thin-layer chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with linear photodiode array detection (LPDA) were used to separate impurities from two commercial dyes. Gravity flow liquid chromatography was used to purify reference standards of t... |
|
|
Disposition and metabolism of 14C-solvent yellow and solvent green aerosols after inhalation.
Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 7(1) , 170-8, (1986) Solvent yellow (2-(2'-quinolinyl)-1,3-indandione) and solvent green (1,4-di-p-toluidinoanthraquinone) are components of colored smoke munitions and may become airborne and be inhaled by workers during the manufacture of the munitions. Little is known about th... |
|
|
Allergic contact dermatitis to D & C yellow 11 in a hair cream.
Contact Dermatitis 17(1) , 57-8, (1987)
|
|
|
Allergy to yellow dyes.
Arch. Dermatol. 120(4) , 535-6, (1984)
|
|
|
Liquid chromatographic determination of 2-(2-quinolinyl)-1H-indene-1,3-[2H]-dione and other organic-soluble matter in D&C Yellow No. 10.
J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 68(3) , 477-9, (1985) A sensitive, reproducible method that uses an Extrelut QE column and liquid chromatography (LC) in the reverse phase mode is described for the determination of 2-(2-quinolinyl)-1H-indene-1,3-[2H]-dione and other organic-soluble matter found in D&C Yellow No. ... |
|
|
Effects of D&C yellow no. 11 ingestion on F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice.
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 48(2) , 197-213, (1996) D&C yellow no. 11 (CAS no. 8003-22-3) was administered in the feed at concentrations of 500-50,000 ppm to groups of F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice of each sex for 13 wk to determine the toxicity. In addition, a perinatal study was conducted to determine the effe... |