FA-Phe-Gly-Gly-OH
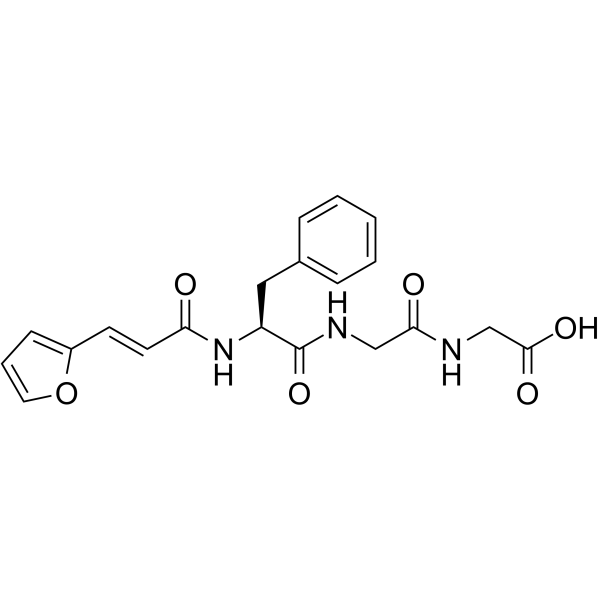
FA-Phe-Gly-Gly-OH structure
|
Common Name | FA-Phe-Gly-Gly-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64967-39-1 | Molecular Weight | 399.397 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 842.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H21N3O6 | Melting Point | 245ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 463.2±34.3 °C | |
|
Effect of power ultrasound pretreatment on peptidic profiles and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition of milk protein concentrate hydrolysates.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 94(12) , 2420-8, (2014) The use of power ultrasound as a pretreatment to enhance the hydrolysis of milk protein concentrate (MPC) and subsequent angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity has been studied. Liquid chromatography was used to analyse peptide profiles of Ne... |
|
|
Assessment and optimization of kinetic methods for angiotensin-converting enzyme in plasma.
Clin. Chem. 39(2) , 312-6, (1993) In the kinetic angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) method, a practical and optimal buffer is 80 mmol/L borate buffer at pH 8.2 (37 degrees C). A lag phase is detected in the reaction, and a 5-min incubation of substrate and plasma is suggested before the kine... |
|
|
Evidence for the negative cooperativity of the two active sites within bovine somatic angiotensin-converting enzyme.
FEBS Lett. 550(1-3) , 84-8, (2003) The somatic isoform of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) consists of two homologous domains (N- and C-domains), each bearing a catalytic site. We have used the two-domain ACE form and its individual domains to compare characteristics of different domains an... |
|
|
Angiotensin-converting enzyme determination in plasma during therapy with converting enzyme inhibitor: two methods compared.
Clin. Chem. 37(8) , 1390-3, (1991) For normal and above-normal concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE; EC 3.4.15.1) activity in plasma, results of a manual fluorometric method [with hippuryl-histidyl-leucine (HHL), 5 mmol/L, as substrate] correlated well with those of an automate... |
|
|
Determination of enzyme (angiotensin convertase) inhibitors based on enzymatic reaction followed by HPLC.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 24(5-6) , 1151-6, (2001) For determination of levels of plasmatic inhibitor of ACE (angiotensin convertase) a simple method was used based on a combination of enzymatic reaction followed by an HPLC determination of its product. The inhibitor (e.g. enalaprilat) was at first separated ... |
|
|
Physiological and enzymatic properties of the ram epididymal soluble form of germinal angiotensin I-converting enzyme.
Biol. Reprod. 65(5) , 1332-9, (2001) The 94-kDa ram epididymal fluid form of the sperm membrane-derived germinal angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) was purified by chromatography, and some of its enzymatic properties were studied. For the artificial substrate furanacryloyl-L-phenylalanylglycy... |
|
|
Pressor and hormonal responses to angiotensin I infusion in healthy subjects of different angiotensin-converting enzyme genotypes.
J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 29(4) , 485-9, (1997) The effects of incremental infusion of angiotensin I on pressor and hormonal responses in relation to the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) genotype were compared in healthy men of genotype DD (n = 8) and II (n = 8). The R(d)25 was the rate of angiotensin I... |
|
|
[Angiotensin-converting enzyme in an OAT-octane reversed micelle system: interaction with the matrix].
Bioorg. Khim. 21(6) , 403-7, (1995) Regulation of catalytic activity and intramolecular structure of the bovine lung angiotensin-converting enzyme was studied using reversed micelles in a sodium docusate-water-octane system, which model the enzyme's environment in vivo. The catalytic parameters... |
|
|
Porcine pulmonary angiotensin I-converting enzyme--biochemical characterization and spatial arrangement of the N- and C-domains by three-dimensional electron microscopic reconstruction.
Micron 41(6) , 674-85, (2010) The somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme (sACE; peptidyl-dipeptidase A; EC 3.4.15.1) was isolated from pig lung and purified to homogeneity. The purified enzyme has a molecular mass of about 180 kDa. Upon proteolytic cleavage, two approximately 90 kDa frag... |
|
|
Carboxypeptidase A hydrolyses benzoylglycyl-histidyl-leucine but not furylacryloyl-phenylalanyl-glycyl-glycine, two usual substrates for angiotensin I-converting enzyme.
Enzyme Protein 48(2) , 81-9, (1994) We compared angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) and carboxypeptidase A (CPA), two zinc metallopeptidases, for the hydrolysis of the usual ACE synthetic substrate benzoylglycyl-histidyl-leucine (HHL) investigating the possible interference by CPA in the dete... |