Dichlorodimethylsilane
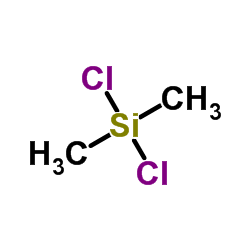
Dichlorodimethylsilane structure
|
Common Name | Dichlorodimethylsilane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-78-5 | Molecular Weight | 129.061 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 70.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6Cl2Si | Melting Point | -76 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | -16.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Interfacial Redox Catalysis on Gold Nanofilms at Soft Interfaces.
ACS Nano 9 , 6565-75, (2015) Soft or "liquid-liquid" interfaces were functionalized by roughly half a monolayer of mirror-like nanofilms of gold nanoparticles using a precise interfacial microinjection method. The surface coverage of the nanofilm was characterized by ion transfer voltamm... |
|
|
Collapse of Particle-Laden Interfaces under Compression: Buckling vs Particle Expulsion.
Langmuir 31 , 7764-75, (2015) Colloidal particles can bind to fluid interfaces with a capillary energy that is thousands of times the thermal energy. This phenomenon offers an effective route to emulsion and foam stabilization where the stability is influenced by the phase behavior of the... |
|
|
Decoupling the contribution of surface energy and surface area on the cohesion of pharmaceutical powders.
Pharm. Res. 32(1) , 248-59, (2015) Surface area and surface energy of pharmaceutical powders are affected by milling and may influence formulation, performance and handling. This study aims to decouple the contribution of surface area and surface energy, and to quantify each of these factors, ... |
|
|
Endogenous fatty acids in olfactory hairs influence pheromone binding protein structure and function in Lymantria dispar.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 579 , 73-84, (2015) The gypsy moth utilizes a pheromone, (7R,8S)-2-methyl-7,8-epoxyoctadecane, for mate location. The pheromone is detected by sensory hairs (sensilla) on the antennae of adult males. Sensilla contain the dendrites of olfactory neurons bathed in lymph, which cont... |
|
|
Effect of plasma treatment on the performance of two drug-loaded hydrogel formulations for therapeutic contact lenses.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. Appl. Biomater. 103 , 1059-68, (2015) Although the plasma technology has long been applied to treat contact lenses, the effect of this treatment on the performance of drug-loaded contact lenses is still unclear. The objective of this work is to study the effect of nitrogen plasma treatment on two... |
|
|
Imprinted Contact Lenses for Sustained Release of Polymyxin B and Related Antimicrobial Peptides.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104 , 3386-94, (2015) The aim of this work was to develop drug-soft contact lens combination products suitable for controlled release of antimicrobial peptides on the ocular surface. Incorporation of functional monomers and the application of molecular imprinting techniques were e... |
|
|
Active food packaging based on molecularly imprinted polymers: study of the release kinetics of ferulic acid.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(46) , 11215-21, (2014) A novel active packaging based on molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was developed for the controlled release of ferulic acid. The release kinetics of ferulic acid from the active system to food simulants (10, 20, and 50% ethanol (v/v), 3% acetic acid (w/v),... |
|
|
Nano-colloid printing of functionalized PLA-b-PEO copolymers: tailoring the surface pattern of adhesive motif and its effect on cell attachment.
Physiol. Res. 64 Suppl 1 , S61-73, (2015) In this study, we investigate the preparation of surface pattern of functional groups on poly(lactide) (PLA) surfaces through the controlled deposition of core-shell self-assemblies based on functionalized PLA-b-PEO amphiphilic block copolymers from selective... |
|
|
K(+) accumulation in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the salt gland cells of Limonium bicolor accompanies increased rates of salt secretion under NaCl treatment using NanoSIMS.
Plant Sci. 238 , 286-96, (2015) Recretohalophytes with specialized salt-secreting structures (salt glands) can secrete excess salts from plant, while discriminating between Na(+) and K(+). K(+)/Na(+) ratio plays an important role in plant salt tolerance, but the distribution and role of K(+... |
|
|
Controlling drug delivery kinetics from mesoporous titania thin films by pore size and surface energy.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 10 , 4425-36, (2015) The osseointegration capacity of bone-anchoring implants can be improved by the use of drugs that are administrated by an inbuilt drug delivery system. However, to attain superior control of drug delivery and to have the ability to administer drugs of varying... |