Dichlorodimethylsilane
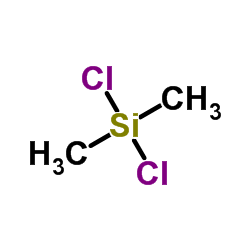
Dichlorodimethylsilane structure
|
Common Name | Dichlorodimethylsilane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-78-5 | Molecular Weight | 129.061 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 70.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6Cl2Si | Melting Point | -76 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | -16.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Dichlorodimethylsilane |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 70.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -76 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6Cl2Si |
| Molecular Weight | 129.061 |
| Flash Point | -16.1±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 127.961578 |
| LogP | 3.18 |
| Vapour Pressure | 142.6±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.410 |
| InChIKey | LIKFHECYJZWXFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C[Si](C)(Cl)Cl |
| Stability | Stable. Reacts violently with water and alcohols. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, water, alcohols, caustics, ammonia. |
| Water Solubility | reacts |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302-H314-H331 |
| Supplemental HS | Corrosive to the respiratory tract., Reacts violently with water. |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F:Flammable |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S60-S61-S62-S36/37-S59 |
| RIDADR | UN 2924 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VV3150000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| HS Code | 29310095 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 29310095 |
|---|
|
Interfacial Redox Catalysis on Gold Nanofilms at Soft Interfaces.
ACS Nano 9 , 6565-75, (2015) Soft or "liquid-liquid" interfaces were functionalized by roughly half a monolayer of mirror-like nanofilms of gold nanoparticles using a precise interfacial microinjection method. The surface coverag... |
|
|
Collapse of Particle-Laden Interfaces under Compression: Buckling vs Particle Expulsion.
Langmuir 31 , 7764-75, (2015) Colloidal particles can bind to fluid interfaces with a capillary energy that is thousands of times the thermal energy. This phenomenon offers an effective route to emulsion and foam stabilization whe... |
|
|
Decoupling the contribution of surface energy and surface area on the cohesion of pharmaceutical powders.
Pharm. Res. 32(1) , 248-59, (2015) Surface area and surface energy of pharmaceutical powders are affected by milling and may influence formulation, performance and handling. This study aims to decouple the contribution of surface area ... |
| UNII-8TSJ92JX69 |
| EINECS 200-901-0 |
| Silane, dichlorodimethyl- |
| MFCD00000491 |
| Dichlorodimethylsilane |
| Dimethyldichlorosilane [UN1162] [Flammable liquid] |
| DIMETHYLDICHLOROSILANE |
| 4-04-00-04111 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) |
| Dimethyl dichlorosilane |
| Dichloro(dimethyl)silane |
| Dow Corning product Z-1219 |
 CAS#:78-62-6
CAS#:78-62-6 CAS#:1112-39-6
CAS#:1112-39-6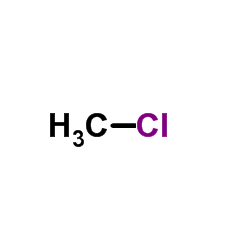 CAS#:74-87-3
CAS#:74-87-3 CAS#:7440-21-3
CAS#:7440-21-3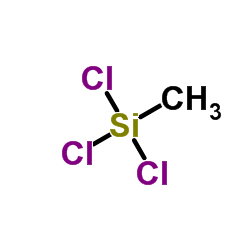 CAS#:75-79-6
CAS#:75-79-6 CAS#:4342-61-4
CAS#:4342-61-4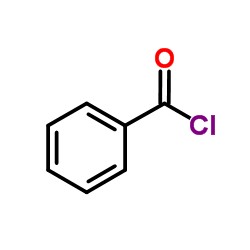 CAS#:98-88-4
CAS#:98-88-4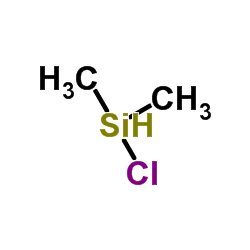 CAS#:1066-35-9
CAS#:1066-35-9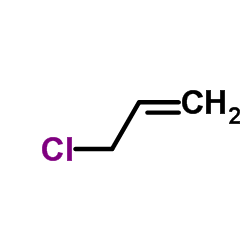 CAS#:107-05-1
CAS#:107-05-1 CAS#:680-31-9
CAS#:680-31-9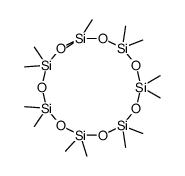 CAS#:107-50-6
CAS#:107-50-6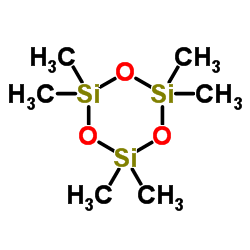 CAS#:541-05-9
CAS#:541-05-9 CAS#:556-67-2
CAS#:556-67-2 CAS#:541-02-6
CAS#:541-02-6 CAS#:540-97-6
CAS#:540-97-6 CAS#:1078-97-3
CAS#:1078-97-3 CAS#:18236-77-6
CAS#:18236-77-6 CAS#:110209-73-9
CAS#:110209-73-9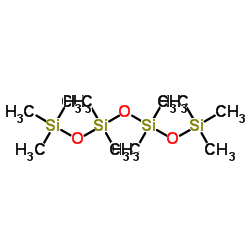 CAS#:141-62-8
CAS#:141-62-8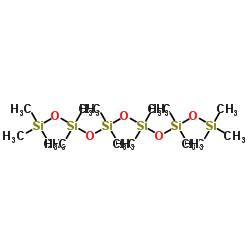 CAS#:107-52-8
CAS#:107-52-8
