2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate
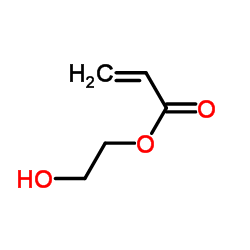
2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate structure
|
Common Name | 2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 818-61-1 | Molecular Weight | 116.115 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 196.2±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O3 | Melting Point | -60 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 98.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Micro-computed tomography image-based evaluation of 3D anisotropy degree of polymer scaffolds.
Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 18(4) , 446-55, (2014) Anisotropy is one of the most meaningful determinants of biomechanical behaviour. This study employs micro-computed tomography (μCT) and image techniques for analysing the anisotropy of regenerative medicine polymer scaffolds. For this purpose, three three-di... |
|
|
Neural tissue regeneration in experimental brain injury model with channeled scaffolds of acrylate copolymers.
Neurosci. Lett. 598 , 96-101, (2015) The objective of the present study was to evaluate the biocompatibility and cell hosting ability of a copolymer scaffold based on ethyl acrylate (EA) and hydroxyl ethyl acrylate (HEA) in vivo after an experimental brain injury. Wistar rats were subjected to c... |
|
|
Photopatterned oil-reservoir micromodels with tailored wetting properties.
Lab Chip 15 , 3047-55, (2015) Micromodels with a simplified porous network that represents geological porous media have been used as experimental test beds for multiphase flow studies in the petroleum industry. We present a new method to fabricate reservoir micromodels with heterogeneous ... |
|
|
Combined application of polyacrylate scaffold and lipoic acid treatment promotes neural tissue reparation after brain injury.
Brain Inj. 30 , 208-16, (2016) The aim of this study was to investigate the reparative potential of a polymeric scaffold designed for brain tissue repair in combination with lipoic acid.Histological, cytological and structural analysis of a combined treatment after a brain cryo-injury mode... |
|
|
Hydroxamic acid-containing hydrogels for nonabsorbed iron chelation therapy: synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation.
Biomacromolecules 6(6) , 2946-53, (2005) Iron overload is a severe clinical condition and can be largely prevented by the use of iron-specific chelating agents. A successful iron chelator needs to be orally active, nontoxic, and selective. In this study, hydrogels containing pendant hydroxamic acid ... |
|
|
The potential dermal irritating effect of residual (meth)acrylic monomers in pressure sensitive adhesive tapes.
Drug Chem. Toxicol. 33(1) , 1-7, (2010) It is generally thought that residual unpolymerized (meth)acrylic monomers commonly found in pressure sensitive adhesive tapes for medical use may cause dermal irritation, but a systematic study has never been carried out. Therefore, we assessed the potential... |
|
|
Macroporous thin membranes for cell transplant in regenerative medicine.
Biomaterials 67 , 254-63, (2015) The aim of this paper is to present a method to produce macroporous thin membranes made of poly (ethyl acrylate-co-hydroxyethyl acrylate) copolymer network with varying cross-linking density for cell transplantation and prosthesis fabrication. The manufacture... |
|
|
Prediction of the "in vivo" mechanical behavior of biointegrable acrylic macroporous scaffolds.
Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 61 , 651-8, (2016) This study examines a biocompatible scaffold series of random copolymer networks P(EA-HEA) made of Ethyl Acrylate, EA, and 2-Hydroxyl Ethyl Acrylate, HEA. The P(EA-HEA) scaffolds have been synthesized with varying crosslinking density and filled with a Poly(V... |
|
|
Peptide gel in a scaffold as a composite matrix for endothelial cells.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 103 , 3293-302, (2015) The performance of a composite environment with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) has been studied to provide an in vitro proof of concept of their potential of being easily vascularized. These cells were seeded in 1 mm thick scaffolds whose por... |
|
|
Structure and properties of methacrylate-endcapped caprolactone networks with modulated water uptake for biomedical applications.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. Appl. Biomater. 83(1) , 266-75, (2007) Methacrylate-endcapped caprolactone (CLMA) networks were synthesized and copolymerized with 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA) seeking to tailor the hydrophilicity of the system. The resulting structure of the copolymer network is investigated by differential scan... |