维生素K3
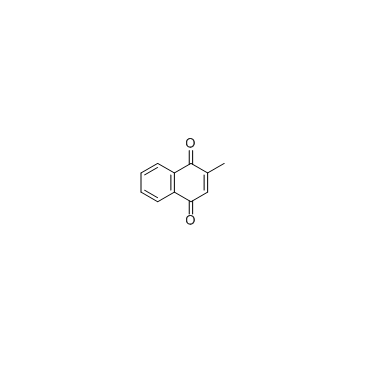
维生素K3结构式

|
常用名 | 维生素K3 | 英文名 | Menadione |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 58-27-5 | 分子量 | 172.18000 | |
| 密度 | 1.225 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 304.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C11H8O2 | 熔点 | 105-107 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 113.8ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Hypoxanthine uptake by skeletal muscle microvascular endothelial cells from equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1)-null mice: effect of oxidative stress.
Microvasc. Res. 98 , 16-22, (2015) Adenosine is an endogenous regulator of vascular tone. This activity of adenosine is terminated by its uptake and metabolism by microvascular endothelial cells (MVEC). The predominant transporter involved is ENT1 (equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype ... |
|
|
Minimal detection of nuclear mutations in XP-V and normal cells treated with oxidative stress inducing agents.
J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 28(12) , 568-77, (2014) Elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) can be induced by exposure to various chemicals and radiation. One type of damage in DNA produced by ROS is modification of guanine to 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG). This particular alteration to the chemis... |
|
|
Time series analysis of oxidative stress response patterns in HepG2: a toxicogenomics approach.
Toxicology 306 , 24-34, (2013) Oxidative stress plays an important role in chemically induced liver injury, however, our insight into molecular responses to different oxygen radicals is fragmentary. Since these cellular responses will differ over time, examining time-dependent changes in g... |
|
|
Oxidative stress modulates nucleobase transport in microvascular endothelial cells
Microvasc. Res. 95 , 68-75, (2014) Purine nucleosides and nucleobases play key roles in the physiological response to vascular ischemia/reperfusion events. The intra- and extracellular concentrations of these compounds are controlled, in part, by equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype 1 ... |
|
|
A graphene/zinc oxide nanocomposite film protects dental implant surfaces against cariogenic Streptococcus mutans.
Biofouling 30(10) , 1281-94, (2014) Oral biofilms play a crucial role in the development of dental caries and other periodontal diseases. Streptococcus mutans is one of the primary etiological agents in dental caries. Implant systems are regularly employed to replace missing teeth. Oral biofilm... |
|
|
Combinatorial effects of arginine and fluoride on oral bacteria.
J. Dent. Res. 94(2) , 344-53, (2015) Dental caries is closely associated with the microbial disequilibrium between acidogenic/aciduric pathogens and alkali-generating commensal residents within the dental plaque. Fluoride is a widely used anticaries agent, which promotes tooth hard-tissue remine... |
|
|
Type II NADH dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain of Plasmodium falciparum and its inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 972-5, (2009) Plasmodium falciparum NDH2 (pfNDH2) is a non-proton pumping, rotenone-insensitive alternative enzyme to the multi-subunit NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductases (Complex I) of many other eukaryotes. Recombinantly expressed pfNDH2 prefers coenzyme CoQ(0) as an accept... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |