双琥珀酰亚胺戊二酸酯
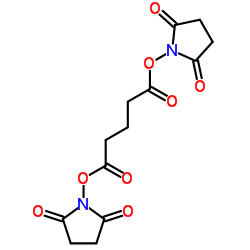
双琥珀酰亚胺戊二酸酯结构式

|
常用名 | 双琥珀酰亚胺戊二酸酯 | 英文名 | DSG Crosslinker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 79642-50-5 | 分子量 | 326.259 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 485.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C13H14N2O8 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 247.2±31.5 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
New insights on the interaction between the isoforms 1 and 2 of human translation elongation factor 1A.
Biochimie 118 , 1-7, (2015) The eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A (eEF1A) is a moonlighting protein that besides to its canonical role in protein synthesis is also involved in many other cellular processes such as cell survival and apoptosis. In a previous work, we identified ... |
|
|
Disruption of STAT3 signalling promotes KRAS-induced lung tumorigenesis.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6285, (2015) STAT3 is considered to play an oncogenic role in several malignancies including lung cancer; consequently, targeting STAT3 is currently proposed as therapeutic intervention. Here we demonstrate that STAT3 plays an unexpected tumour-suppressive role in KRAS mu... |
|
|
The nuclear receptor nr4a1 controls CD8 T cell development through transcriptional suppression of runx3.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 9059, (2015) The NR4A nuclear receptor family member Nr4a1 is strongly induced in thymocytes undergoing selection, and has been shown to control the development of Treg cells; however the role of Nr4a1 in CD8(+) T cells remains undefined. Here we report a novel role for N... |
|
|
The SWI/SNF subunit/tumor suppressor BAF47/INI1 is essential in cell cycle arrest upon skeletal muscle terminal differentiation.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e108858, (2014) Myogenic terminal differentiation is a well-orchestrated process starting with permanent cell cycle exit followed by muscle-specific genetic program activation. Individual SWI/SNF components have been involved in muscle differentiation. Here, we show that the... |
|
|
Longitudinal follow-up and characterization of a robust rat model for Parkinson's disease based on overexpression of alpha-synuclein with adeno-associated viral vectors.
Neurobiol. Aging 36 , 1543-58, (2015) Testing of new therapeutic strategies for Parkinson's disease (PD) is currently hampered by the lack of relevant and reproducible animal models. Here, we developed a robust rat model for PD by injection of adeno-associated viral vectors (rAAV2/7) encoding α-s... |
|
|
Proteins that bind regulatory regions identified by histone modification chromatin immunoprecipitations and mass spectrometry.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7155, (2015) The locations of transcriptional enhancers and promoters were recently mapped in many mammalian cell types. Proteins that bind those regulatory regions can determine cell identity but have not been systematically identified. Here we purify native enhancers, p... |
|
|
RAR/RXR binding dynamics distinguish pluripotency from differentiation associated cis-regulatory elements.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43 , 4833-54, (2015) In mouse embryonic cells, ligand-activated retinoic acid receptors (RARs) play a key role in inhibiting pluripotency-maintaining genes and activating some major actors of cell differentiation. To investigate the mechanism underlying this dual regulation, we p... |
|
|
A critical role for the chromatin remodeller CHD7 in anterior mesoderm during cardiovascular development.
Dev. Biol. 405 , 82-95, (2015) CHARGE syndrome is caused by spontaneous loss-of-function mutations to the ATP-dependant chromatin remodeller chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 7 (CHD7). It is characterised by a distinct pattern of congenital anomalies, including cardiovascular malfo... |
|
|
Membrane-anchored MucR mediates nitrate-dependent regulation of alginate production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 7253-65, (2015) Alginates exhibit unique material properties suitable for medical and industrial applications. However, if produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, it is an important virulence factor in infection of cystic fibrosis patients. The alginate biosynthesis machinery is... |
|
|
Regulation of Transcription Elongation by the XPG-TFIIH Complex Is Implicated in Cockayne Syndrome.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 35 , 3178-88, (2015) XPG is a causative gene underlying the photosensitive disorder xeroderma pigmentosum group G (XP-G) and is involved in nucleotide excision repair. Here, we show that XPG knockdown represses epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced FOS transcription at the level ... |