Epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine
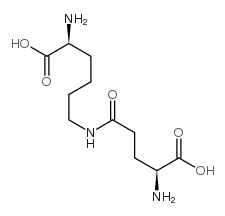
Epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine结构式

|
常用名 | Epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine | 英文名 | H-Glu(H-Lys-OH)-OH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 17105-15-6 | 分子量 | 275.30200 | |
| 密度 | 1.29g/cm3 | 沸点 | 610.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C11H21N3O5 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 322.9ºC |
|
In-vitro digestibility and amino acid composition of soy protein isolate cross-linked with microbial transglutaminase followed by heating with ribose.
Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 Suppl 7 , 99-108, (2009) Cross-linked soy protein isolate (SPI) gels were produced via single-treatment of SPI with microbial transglutaminase (MTG) for 5 h or 24 h, or with ribose for 2 h, or via combined-treatments of SPI with MTG followed by heating with ribose. Assessment of gel ... |
|
|
Inhibition of transglutaminase activity reduces extracellular matrix accumulation induced by high glucose levels in proximal tubular epithelial cells.
J. Biol. Chem. 279(46) , 47754-62, (2004) Diabetic nephropathy affects 30-40% of diabetics leading to end-stage kidney failure through progressive scarring and fibrosis. Previous evidence suggests that tissue transglutaminase (tTg) and its protein cross-link product epsilon(gamma-glutamyl)lysine cont... |
|
|
Identification and quantification of epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine in digests of enzymatically cross-linked leguminous proteins by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS).
J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(8) , 2830-7, (2005) A rapid and convenient method for the precise quantification of epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine isopeptide in lyophilized proteolytic digests of cross-linked plant protein samples was developed. The isopeptide was baseline-separated from three other isomers co... |
|
|
Tissue transglutaminase: a mediator and predictor of chronic allograft nephropathy?
Transplantation 77(11) , 1667-75, (2004) The precise mechanisms underlying the development of chronic allograft nephropathy (CAN) and the associated renal fibrosis remain uncertain. The protein-crosslinking enzyme, tissue transglutaminase (tTg), has recently been implicated in renal fibrosis. METHOD... |
|
|
Tuft protein: protein cross-linking in enamel development.
Eur. J. Oral Sci. 119 Suppl 1 , 50-4, (2011) Tuft protein is a material associated with enamel tufts, and resides in dental enamel primarily at the enamel-dentine junction. It is located primarily at prism peripheries and extends in a very attenuated form towards the enamel outer surface. While it appea... |
|
|
Characterization of a microbial transglutaminase cross-linked type II collagen scaffold.
Tissue Eng. 12(6) , 1467-74, (2006) This study investigated the effect on the mechanical and physicochemical properties of type II collagen scaffolds after cross-linking with microbial transglutaminase (mTGase). It is intended to develop a collagen-based scaffold to be used for the treatment of... |
|
|
Potential role of tissue transglutaminase in glaucoma filtering surgery.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47(9) , 3835-45, (2006) Scarring of the filtering bleb site is the main cause of failure in glaucoma filtration surgery. In the present study, the role of tissue transglutaminase (tTgase) in the accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in these scars was investigated. Tra... |
|
|
Extracellular matrix modifications at fertilization: regulation of dityrosine crosslinking by transamidation.
Development 136(11) , 1835-47, (2009) Fertilization is accompanied by the construction of an extracellular matrix that protects the new zygote. In sea urchins, this structure is built from glycoproteins residing at the egg surface and in secretory vesicles at the egg cortex. Four enzymatic activi... |
|
|
Tools for the detection and quantitation of protein transglutamination.
Anal. Biochem. 342(1) , 1-10, (2005)
|
|
|
γ-Glutamylamines and neurodegenerative diseases.
Amino Acids 44(1) , 129-42, (2013) Transglutaminases catalyze the formation of γ-glutamylamines utilizing glutamyl residues and amine-bearing compounds such as lysyl residues and polyamines. These γ-glutamylamines can be released from proteins by proteases in an intact form. The free γ-glutamy... |