Inhibition of transglutaminase activity reduces extracellular matrix accumulation induced by high glucose levels in proximal tubular epithelial cells.
Nicholas J Skill, Timothy S Johnson, Ian G C Coutts, Robert E Saint, Marie Fisher, Linghong Huang, A Meguid El Nahas, Russell J Collighan, Martin Griffin
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 279(46) , 47754-62, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Diabetic nephropathy affects 30-40% of diabetics leading to end-stage kidney failure through progressive scarring and fibrosis. Previous evidence suggests that tissue transglutaminase (tTg) and its protein cross-link product epsilon(gamma-glutamyl)lysine contribute to the expanding renal tubulointerstitial and glomerular basement membranes in this disease. Using an in vitro cell culture model of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells we determined the link between elevated glucose levels with changes in expression and activity of tTg and then, by using a highly specific site directed inhibitor of tTg (1,3-dimethyl-2[(oxopropyl)thio]imidazolium), determined the contribution of tTg to glucose-induced matrix accumulation. Exposure of cells to 36 mm glucose over 96 h caused an mRNA-dependent increase in tTg activity with a 25% increase in extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated tTg and a 150% increase in ECM epsilon(gamma-glutamyl)lysine cross-linking. This was paralleled by an elevation in total deposited ECM resulting from higher levels of deposited collagen and fibronectin. These were associated with raised mRNA for collagens III, IV, and fibronectin. The specific site-directed inhibitor of tTg normalized both tTg activity and ECM-associated epsilon(gamma-glutamyl)lysine. Levels of ECM per cell returned to near control levels with non-transcriptional reductions in deposited collagen and fibronectin. No changes in transforming growth factor beta1 (expression or biological activity) occurred that could account for our observations, whereas incubation of tTg with collagen III indicated that cross-linking could directly increase the rate of collagen fibril/gel formation. We conclude that Tg inhibition reduces glucose-induced deposition of ECM proteins independently of changes in ECM and transforming growth factor beta1 synthesis thus opening up its possible application in the treatment other fibrotic and scarring diseases where tTg has been implicated.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
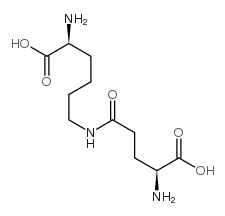 |
Epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine
CAS:17105-15-6 |
C11H21N3O5 |
|
In-vitro digestibility and amino acid composition of soy pro...
2009-01-01 [Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 Suppl 7 , 99-108, (2009)] |
|
Identification and quantification of epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl...
2005-04-20 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(8) , 2830-7, (2005)] |
|
Tissue transglutaminase: a mediator and predictor of chronic...
2004-06-15 [Transplantation 77(11) , 1667-75, (2004)] |
|
Tuft protein: protein cross-linking in enamel development.
2011-12-01 [Eur. J. Oral Sci. 119 Suppl 1 , 50-4, (2011)] |
|
Characterization of a microbial transglutaminase cross-linke...
2006-06-01 [Tissue Eng. 12(6) , 1467-74, (2006)] |