4-氯水杨酸
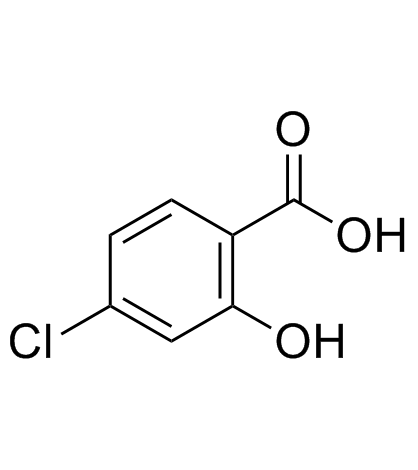
4-氯水杨酸结构式

|
常用名 | 4-氯水杨酸 | 英文名 | 4-Chlorosalicylic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 5106-98-9 | 分子量 | 172.566 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 321.1±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C7H5ClO3 | 熔点 | 210-212 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 148.0±23.7 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
New bacterial pathway for 4- and 5-chlorosalicylate degradation via 4-chlorocatechol and maleylacetate in Pseudomonas sp. strain MT1.
J. Bacteriol. 185(23) , 6790-800, (2003) Pseudomonas sp. strain MT1 is capable of degrading 4- and 5-chlorosalicylates via 4-chlorocatechol, 3-chloromuconate, and maleylacetate by a novel pathway. 3-Chloromuconate is transformed by muconate cycloisomerase of MT1 into protoanemonin, a dominant reacti... |
|
|
Two angular dioxygenases contribute to the metabolic versatility of dibenzofuran-degrading Rhodococcus sp. strain HA01.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74(12) , 3812-22, (2008) Rhodococcus sp. strain HA01, isolated through its ability to utilize dibenzofuran (DBF) as the sole carbon and energy source, was also capable, albeit with low activity, of transforming dibenzo-p-dioxin (DD). This strain could also transform 3-chlorodibenzofu... |
|
|
Consortia modulation of the stress response: proteomic analysis of single strain versus mixed culture.
Environ. Microbiol. 12(9) , 2436-49, (2010) The high complexity of naturally occurring microbial communities is the major drawback limiting the study of these important biological systems. In this study, a comparison between pure cultures of Pseudomonas reinekei sp. strain MT1 and stable community cult... |
|
|
Spectrofluorometric determination of trace amounts of terbium with 4-chlorosalicylic acid, EDTA, and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.
Anal. Sci. 19(6) , 923-5, (2003) The quadruple complex formed by terbium with 4-chlorosalicylic acid (CSA), EDTA and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTMAB) has been used for the sensitive spectrofluorometric determination of terbium in mixed rare earths. The effect of the experimental condit... |
|
|
Bacterial consortium proteomics under 4-chlorosalicylate carbon-limiting conditions.
Proteomics 9(8) , 2273-85, (2009) In this study, the stable consortium composed by Pseudomonas reinekei strain MT1 and Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain MT3 (cell numbers in proportion 9:1) was under investigation to reveal bacterial interactions that take place under severe nutrient-limiting... |
|
|
Community-based degradation of 4-chorosalicylate tracked on the single cell level.
J. Microbiol. Methods 75(1) , 117-26, (2008) 4-Chlorosalicylate (4-CS) can be degraded completely by a bacterial consortium consisting of Pseudomonas reinekei (MT1), Achromobacter spanius (MT3) and Pseudomonas veronii (MT4). The fourth species Wautersiella falsenii (MT2) is thought to act as a 'necrotiz... |
|
|
Inhibitory effects of 4-chlorosalicylic acid on mushroom tyrosinase and its antimicrobial activities. Han P, et al.
Food Chem. 107(2) , 797-803, (2008)
|
|
|
4-Chlorosalicylic acid-formaldehyde polymer as a polymeric ligand. Patel HS, et al.
Makromol. Chem. 106(1) , 223-237, (1982)
|