4-Chlorosalicylic acid
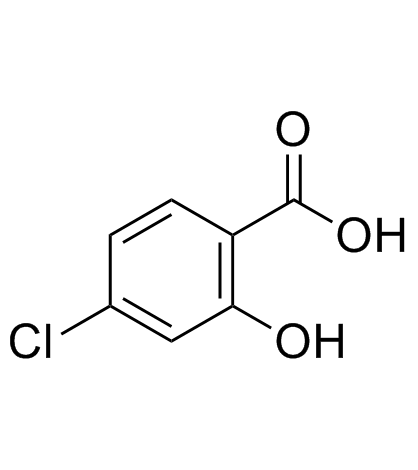
4-Chlorosalicylic acid structure
|
Common Name | 4-Chlorosalicylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5106-98-9 | Molecular Weight | 172.566 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 321.1±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5ClO3 | Melting Point | 210-212 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 148.0±23.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 4-Chlorosalicylic acid4-Chlorosalicylic acid is a pharmaceutical intermediate. Inhibits monophenolase and diphenolase activity with IC50s of 1.89 mM and 1.10 mM. Potent antimicrobial activity. Against E. coli with the MIC of 250 μg/mL and with the MBC of 500 μg/mL. |
| Name | 4-Chlorosalicylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-Chlorosalicylic acid is a pharmaceutical intermediate. Inhibits monophenolase and diphenolase activity with IC50s of 1.89 mM and 1.10 mM. Potent antimicrobial activity. Against E. coli with the MIC of 250 μg/mL and with the MBC of 500 μg/mL. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 1.89 mM (monophenolase), 1.10 mM (diphenolase)[1] |
| In Vitro | 4-chlorosalicylic acid could inhibit both the diphenolase activity and the monophenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase. 4-chlorosalicylic acid has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity which could inhibits Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and fungi[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 321.1±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 210-212 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5ClO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 172.566 |
| Flash Point | 148.0±23.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 171.992722 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 3.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.630 |
| InChIKey | LWXFCZXRFBUOOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)c1ccc(Cl)cc1O |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2918219000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
New bacterial pathway for 4- and 5-chlorosalicylate degradation via 4-chlorocatechol and maleylacetate in Pseudomonas sp. strain MT1.
J. Bacteriol. 185(23) , 6790-800, (2003) Pseudomonas sp. strain MT1 is capable of degrading 4- and 5-chlorosalicylates via 4-chlorocatechol, 3-chloromuconate, and maleylacetate by a novel pathway. 3-Chloromuconate is transformed by muconate ... |
|
|
Two angular dioxygenases contribute to the metabolic versatility of dibenzofuran-degrading Rhodococcus sp. strain HA01.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74(12) , 3812-22, (2008) Rhodococcus sp. strain HA01, isolated through its ability to utilize dibenzofuran (DBF) as the sole carbon and energy source, was also capable, albeit with low activity, of transforming dibenzo-p-diox... |
|
|
Consortia modulation of the stress response: proteomic analysis of single strain versus mixed culture.
Environ. Microbiol. 12(9) , 2436-49, (2010) The high complexity of naturally occurring microbial communities is the major drawback limiting the study of these important biological systems. In this study, a comparison between pure cultures of Ps... |
| 4-Chloro Salicylic Acid |
| 4-Chloro-2-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid |
| MFCD00002449 |
| Benzoic acid, 4-chloro-2-hydroxy- |
| 4-Chlorosalicylic Acid |
| 4-Chloro-2-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| EINECS 225-829-7 |
 CAS#:74-11-3
CAS#:74-11-3 CAS#:50-84-0
CAS#:50-84-0 CAS#:108-43-0
CAS#:108-43-0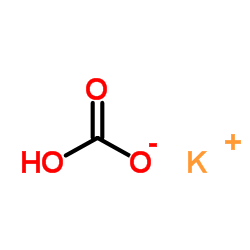 CAS#:298-14-6
CAS#:298-14-6 CAS#:5900-59-4
CAS#:5900-59-4 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9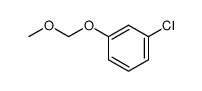 CAS#:91105-99-6
CAS#:91105-99-6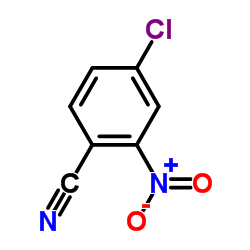 CAS#:34662-32-3
CAS#:34662-32-3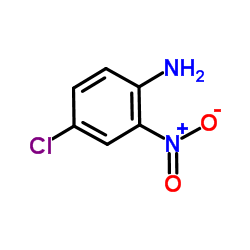 CAS#:89-63-4
CAS#:89-63-4 CAS#:135251-11-5
CAS#:135251-11-5 CAS#:212892-02-9
CAS#:212892-02-9 CAS#:2420-26-0
CAS#:2420-26-0 CAS#:78955-90-5
CAS#:78955-90-5 CAS#:89-56-5
CAS#:89-56-5![6-Chlorobenzo[D]Isoxazol-3-Ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/066/61977-29-5.png) CAS#:61977-29-5
CAS#:61977-29-5 CAS#:142167-38-2
CAS#:142167-38-2![3,6-Dichlorobenzo[d]isoxazole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/189/16263-54-0.png) CAS#:16263-54-0
CAS#:16263-54-0 CAS#:22717-55-1
CAS#:22717-55-1 CAS#:64917-81-3
CAS#:64917-81-3 CAS#:82944-13-6
CAS#:82944-13-6
