戊诺酰胺
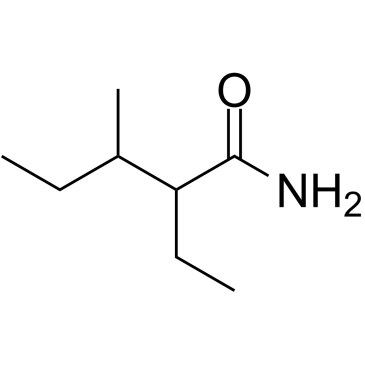
戊诺酰胺结构式

|
常用名 | 戊诺酰胺 | 英文名 | Valnoctamide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 4171-13-5 | 分子量 | 143.22700 | |
| 密度 | 0.883g/cm3 | 沸点 | 274.4ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H17NO | 熔点 | 113.5-114ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 119.8ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Structure activity relationship of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase inhibition by amide and acid analogues of valproic acid.
Pharm. Res. 17(2) , 216-21, (2000) The purpose of this study was to evaluate the in vitro inhibitory potency of various amide analogues and derivatives of valproic acid toward human microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH).mEH inhibition was evaluated in human liver microsomes with 25 microM (S)-(+)... |
|
|
A comparative electrographic analysis of the effect of sec-butyl-propylacetamide on pharmacoresistant status epilepticus.
Neuroscience 231 , 145-56, (2013) Better treatment of status epilepticus (SE), which typically becomes refractory after about 30 min, will require new pharmacotherapies. The effect of sec-butyl-propylacetamide (SPD), an amide derivative of valproic acid (VPA), on electrographic status epilept... |
|
|
Amidic modification of valproic acid reduces skeletal teratogenicity in mice.
Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 71(1) , 47-53, (2004) The antiepileptic drug valproic acid (VPA) is well known to cause neural tube and skeletal defects in both humans and animals. The amidic VPA analogues valpromide (VPD) and valnoctamide (VCD) have much lower teratogenicity than VPA inducing exencephaly in mic... |
|
|
Polycomb homologs are involved in teratogenicity of valproic acid in mice.
Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 70(11) , 870-9, (2004) Valproic acid (VPA) is widely used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and is also a potent teratogen, but its teratogenic mechanisms are unknown. We have attempted to describe a fundamental role of the Polycomb group (Pc-G) in VPA-induced transformations ... |
|
|
Identification of early-responsive genes correlated to valproic acid-induced neural tube defects in mice.
Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 73(4) , 229-38, (2005) Valproic acid (VPA) causes the failure of neural tube closure in newborn mice. However, the molecular mechanism of its teratogenesis is unknown. This study was conducted to investigate the genomewide effects of VPA disruption of normal neural tube development... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of a valpromide isomer, valnoctamide, in healthy subjects.
Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 38(3) , 289-91, (1990) The pharmacokinetics of a single 400 mg oral dose of valnoctamide (VCD) has been investigated in seven healthy, adult, male volunteers. VCD was not biotransformed rapidly to its corresponding acid valnoctic acid (VCA), unlike its isomer valpromide (VPD). It h... |
|
|
In vivo study of the effect of valpromide and valnoctamide in the pilocarpine rat model of focal epilepsy.
Pharm. Res. 17(11) , 1408-13, (2000) We evaluated the effectiveness of the commonly used antiepileptic drug sodium valproate (400 mg/kg) and two of its amide derivatives, valpromide and valnoctamide (both 100 mg/kg), in an in vivo rat model of focal epilepsy. Our main interest was to get insight... |
|
|
Valnoctamide as a valproate substitute with low teratogenic potential in mania: a double-blind, controlled, add-on clinical trial.
Bipolar Disord. 12(4) , 376-82, (2010) Valproic acid's well-known teratogenicity limits its use in women of childbearing age. Valnoctamide is an analog of valproate that does not undergo biotransformation to the corresponding free acid. In mice, valnoctamide has been shown to be distinctly less te... |
|
|
Stereoselective pharmacokinetic analysis of valnoctamide, a CNS-active chiral amide analogue of valproic acid, in dogs, rats, and mice.
Ther. Drug Monit. 22(5) , 574-81, (2000) The purpose of this study was to evaluate the stereoselective pharmacokinetics of valnoctamide (VCD) in dogs, rats, and mice; which are the most common animal models for pharmacokinetic, pharmacologic, and toxicologic evaluation; and to compare it with previo... |
|
|
A new derivative of valproic acid amide possesses a broad-spectrum antiseizure profile and unique activity against status epilepticus and organophosphate neuronal damage.
Epilepsia 53(1) , 134-46, (2012) sec-Butyl-propylacetamide (SPD) is a one-carbon homolog of valnoctamide (VCD), a central nervous system (CNS)-active amide derivative of valproic acid (VPA) currently in phase II clinical trials. The study reported herein evaluated the anticonvulsant activity... |