Stereoselective pharmacokinetic analysis of valnoctamide, a CNS-active chiral amide analogue of valproic acid, in dogs, rats, and mice.
O Spiegelstein, B Yagen, G D Bennett, R H Finnell, S Blotnik, M Bialer
文献索引:Ther. Drug Monit. 22(5) , 574-81, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the stereoselective pharmacokinetics of valnoctamide (VCD) in dogs, rats, and mice; which are the most common animal models for pharmacokinetic, pharmacologic, and toxicologic evaluation; and to compare it with previously published human data. Racemic VCD (mixture of four stereoisomers) was administered intravenously to six mongrel dogs and to rats (five rats per time-point), and intraperitoneally to mice (five mice per time-point). Plasma concentrations of the individual stereoisomers were measured by a stereospecific gas chromatography assay. In dogs, (2S,3R)-VCD had a larger clearance (0.33 L/h x kg) and a larger volume of distribution (0.79 L/kg) than its two diastereomers (0.24-0.25 L/h x kg and 0.65 L/kg, respectively). A tendency toward slightly higher clearance and volume of distribution values for (2S,3R)-VCD was observed in rats and mice as well. Consequently, in all three animal species the half-life (t1/2) of (2S,3R)-VCD was not different from the t1/2 of the other three VCD stereoisomers. The stereoselective pharmacokinetics of VCD as observed in dogs, rats, and mice is in line with the stereoselectivity previously observed in healthy subjects and epileptic patients.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
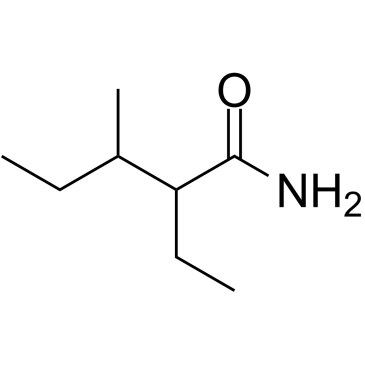 |
戊诺酰胺
CAS:4171-13-5 |
C8H17NO |
|
Structure activity relationship of human microsomal epoxide ...
2000-02-01 [Pharm. Res. 17(2) , 216-21, (2000)] |
|
A comparative electrographic analysis of the effect of sec-b...
2013-02-12 [Neuroscience 231 , 145-56, (2013)] |
|
Amidic modification of valproic acid reduces skeletal terato...
2004-02-01 [Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 71(1) , 47-53, (2004)] |
|
Polycomb homologs are involved in teratogenicity of valproic...
2004-11-01 [Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 70(11) , 870-9, (2004)] |
|
Identification of early-responsive genes correlated to valpr...
2005-04-01 [Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 73(4) , 229-38, (2005)] |