甲基紫精
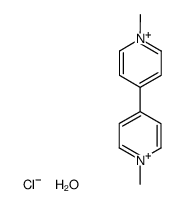
甲基紫精结构式

|
常用名 | 甲基紫精 | 英文名 | Methyl viologen dichloride hydrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 75365-73-0 | 分子量 | 239.72100 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C12H16ClN2O+ | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A | |
| 符号 |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Functional cloning and characterization of the multidrug efflux pumps NorM from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and YdhE from Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 3052-60, (2008) Active efflux of antimicrobial agents is one of the most important adapted strategies that bacteria use to defend against antimicrobial factors that are present in their environment. The NorM protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the YdhE protein of Escherichi... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Evaluation of a published in silico model and construction of a novel Bayesian model for predicting phospholipidosis inducing potential.
J. Chem. Inf. Model. 47 , 1196-205, (2007) The identification of phospholipidosis (PPL) during preclinical testing in animals is a recognized problem in the pharmaceutical industry. Depending on the intended indication and dosing regimen, PPL can delay or stop development of a compound in the drug dis... |
|
|
Development of a phospholipidosis database and predictive quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models.
Toxicol. Mech. Methods 18 , 217-27, (2008) ABSTRACT Drug-induced phospholipidosis (PL) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of phospholipids and drug in lysosomes, and is found in a variety of tissue types. PL is frequently manifested in preclinical studies and may delay or prevent the dev... |
|
|
Genetic, molecular and physiological basis of variation in Drosophila gut immunocompetence.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7829, (2015) Gut immunocompetence involves immune, stress and regenerative processes. To investigate the determinants underlying inter-individual variation in gut immunocompetence, we perform enteric infection of 140 Drosophila lines with the entomopathogenic bacterium Ps... |
|
|
Role of AbeS, a novel efflux pump of the SMR family of transporters, in resistance to antimicrobial agents in Acinetobacter baumannii.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 5312-6, (2009) In this study, a chromosomally encoded putative drug efflux pump of the SMR family, named AbeS, from a multidrug-resistant strain of Acinetobacter baumannii was characterized to elucidate its role in antimicrobial resistance. Expression of the cloned abeS gen... |
|
|
An early response to environmental stress involves regulation of OmpX and OmpF, two enterobacterial outer membrane pore-forming proteins.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 3190-8, (2007) Bacterial adaptation to external stresses and toxic compounds is a key step in the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains that are a serious threat to human health. Although some of the proteins and regulators involved in antibiotic resistance mechanisms ha... |
|
|
Benzodiazepinone derivatives protect against endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death in human neuronal cell lines.
ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6(3) , 464-75, (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress causes neuronal dysfunction followed by cell death and is recognized as a feature of many neurodegenerative diseases. Using a phenotypic screen, we recently identified benzodiazepinone derivatives that reduce ER stress-mediat... |
|
|
Role of electron transport chain of chloroplasts in oxidative burst of interaction between Erwinia amylovora and host cells.
Photosynth. Res. 124(2) , 231-42, (2015) Erwinia amylovora is a necrogenic bacterium, causing the fire blight disease on many rosaceous plants. Triggering oxidative burst by E. amylovora is a key response by which host plants try to restrain pathogen spread. Electron transport chain (ETC) of chlorop... |