| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
磷化氢
CAS:7803-51-2 |
|
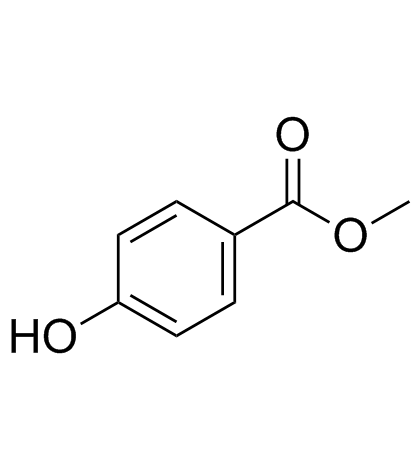 |
尼泊金甲酯
CAS:99-76-3 |
|
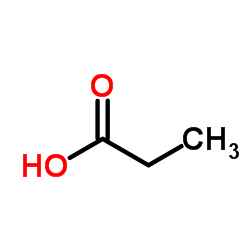 |
丙酸
CAS:79-09-4 |
|
 |
赤磷
CAS:7723-14-0 |
|
 |
4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚二盐酸盐
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
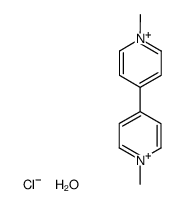 |
甲基紫精
CAS:75365-73-0 |