四氢姜黄素
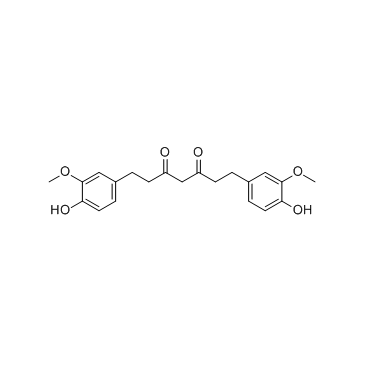
四氢姜黄素结构式

|
常用名 | 四氢姜黄素 | 英文名 | Tetrahydrocurcumin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 36062-04-1 | 分子量 | 372.412 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 564.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C21H24O6 | 熔点 | 95-97ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 196.2±22.2 °C |
|
Structure-activity relationship analysis of curcumin analogues on anti-influenza virus activity.
FEBS J. 280(22) , 5829-40, (2013) Curcumin (Cur) is a commonly used colouring agent and spice in food. Previously, we reported that Cur inhibits type A influenza virus (IAV) infection by interfering with viral haemagglutination (HA) activity. To search for a stable Cur analogue with potent an... |
|
|
Differential cellular uptake and metabolism of curcuminoids in monocytes/macrophages: regulatory effects on lipid accumulation.
Br. J. Nutr. 112(1) , 8-14, (2014) We have previously shown that curcumin (CUR) may increase lipid accumulation in cultured human acute monocytic leukaemia cell line THP-1 monocytes/macrophages, but that tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), an in vivo metabolite of CUR, has no such effect. In the present... |
|
|
Synthesis of quinoline derivatives of tetrahydrocurcumin and zingerone and evaluation of their antioxidant and antibacterial attributes.
Food Chem. 136(2) , 650-8, (2013) Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC, 1) and zingerone (2) are biologically active molecules originating from the important spices turmeric and ginger, respectively. Novel quinoline derivatives of THC and zingerone have been synthesised by an efficient protocol involving ... |
|
|
Antioxidant combinations protect oral fibroblasts against metal-induced toxicity.
Arch. Oral Biol. 58(3) , 299-310, (2013) In dentistry, the use of metals in fillings, braces, implants, bridges and other prosthodontic restorations is a common practice. Previous studies revealed that zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) released from gold alloys, and nickel (Ni) released from nickel-chromium... |
|
|
Inhibition of Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) channel (CRAC) by curcumin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) via electrophilic addition to a cysteine residue of Orai1.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 428(1) , 56-61, (2012) Ca(2+) influx through Ca(2+)-release activated Ca(2+) channels (CRAC) is critical for activating immune cells. Orai and STIM proteins comprise the molecular components of CRAC. We previously observed that curcumin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) inhib... |
|
|
Combined treatment of tetrahydrocurcumin and chlorogenic acid exerts potential antihyperglycemic effect on streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats.
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 29(1) , 23-30, (2010) We have shown that separate dose of tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) at a dose of 80 mg/kg body weight (b.w.) and chlorogenic acid (CGA) at a dose of 5 mg/kg b.w. exerts antidiabetic potential in streptozotocin (STZ) (45 mg/kg b.w.) nicotinamide induced diabetic rats... |
|
|
Tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorates homocysteinylated cytochrome-c mediated autophagy in hyperhomocysteinemia mice after cerebral ischemia.
J. Mol. Neurosci. 47(1) , 128-38, (2012) High levels of homocysteine (Hcy) known as hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), contribute to autophagy and ischemia/reperfusion injury (I/R). Previous studies have shown that I/R injury and HHcy cause increased cerebrovascular permeability; however, the associated m... |
|
|
In vitro inhibitory effect of tetrahydrocurcuminoids on Fusarium proliferatum growth and fumonisin B₁ biosynthesis.
Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 28(2) , 218-25, (2011) Many plant pathogens produce toxic metabolites when growing on food and feed. Some antioxidative components seem to prevent fungal growth and mycotoxin formation. Recently, we synthesized a new class of powerful antioxidative compounds, i.e. tetrahydrocurcumi... |
|
|
Tetrahydrocurcumin confers protection against amyloid β-induced toxicity.
Neuroreport 22(1) , 23-7, (2011) Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. Amyloid β, a primary component of the amyloid plaques, is neurotoxic. Considerable attention has been directed toward identifying compounds with neuroprotective properties. ... |
|
|
Tissue distribution of (Lipocurc™) liposomal curcumin and tetrahydrocurcumin following two- and eight-hour infusions in Beagle dogs.
Anticancer Res. 32(10) , 4359-64, (2012) This study interrogated whether different durations of intravenous infusions of lipocurc™ would alter curcumin metabolism, tissue distribution and whether treating necropsied tissues of Beagle dogs with phosphoric acid prior to measuring curcumin and its meta... |