Tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorates homocysteinylated cytochrome-c mediated autophagy in hyperhomocysteinemia mice after cerebral ischemia.
Neetu Tyagi, Natia Qipshidze, Charu Munjal, Jonathan C Vacek, Naira Metreveli, Srikanth Givvimani, Suresh C Tyagi
文献索引:J. Mol. Neurosci. 47(1) , 128-38, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
High levels of homocysteine (Hcy) known as hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), contribute to autophagy and ischemia/reperfusion injury (I/R). Previous studies have shown that I/R injury and HHcy cause increased cerebrovascular permeability; however, the associated mechanism remains obscure. Interestingly, during HHcy, cytochome-c becomes homocysteinylated (Hcy-cyto-c). Cytochrome-c (cyto-c) transports electrons and facilitates bioenergetics in the system. However, its role in autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion injury is unclear. Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) is a major herbal antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine whether THC ameliorates autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing homocysteinylation of cyto-c in hyperhomocysteinemia pathological condition. To test this hypothesis, we employed 8-10-week-old male cystathionine-beta-synthase heterozygote knockout (CBS⁺/⁻) mice (genetically hyperhomocystemic mice). Experimental group was: CBS⁺/⁻, CBS⁺/⁻ + THC (25 mg/kg in 0.1% DMSO dose); CBS ⁺/⁻/I/R, and CBS⁺/⁻/I/R + THC (25 mg/kg in 0.1% DMSO dose). Ischemia was performed for 30 min and reperfusion for 72 h. THC was injected intra-peritoneally (I.P.) once daily for a period of 3 days after 30 min of ischemia. The infarct area was measured using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. Permeability was determined by brain edema and Evans Blue extravasation. The brain tissues were analyzed for oxidative stress, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), damage-regulated autophagy modulator (DRAM), and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) by Western blot. The mRNA levels of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolases (SAHH) and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) genes were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to determine the homocysteinylation of cyto-c. We found that brain edema and Evans Blue leakage were reduced in I/R + THC-treated groups as compared to sham-operated groups along with reduced brain infarct size. THC also decreased oxidative damage and ameliorated the homocysteinylation of cyto-c in-part by MMP-9 activation which leads to autophagy in I/R groups as compared to sham-operated groups. This study suggests a potential therapeutic role of dietary THC in cerebral ischemia.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
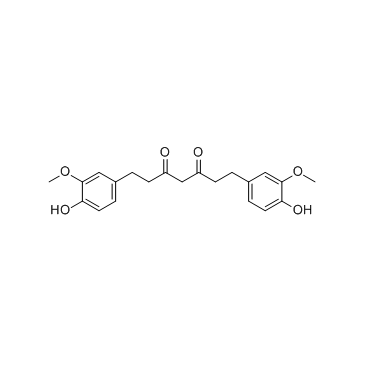 |
四氢姜黄素
CAS:36062-04-1 |
C21H24O6 |
|
Structure-activity relationship analysis of curcumin analogu...
2013-11-01 [FEBS J. 280(22) , 5829-40, (2013)] |
|
Differential cellular uptake and metabolism of curcuminoids ...
2014-07-14 [Br. J. Nutr. 112(1) , 8-14, (2014)] |
|
Synthesis of quinoline derivatives of tetrahydrocurcumin and...
2013-01-15 [Food Chem. 136(2) , 650-8, (2013)] |
|
Antioxidant combinations protect oral fibroblasts against me...
2013-03-01 [Arch. Oral Biol. 58(3) , 299-310, (2013)] |
|
Inhibition of Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) channel (CRAC)...
2012-11-09 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 428(1) , 56-61, (2012)] |