S-烯丙基-L-半胱氨酸
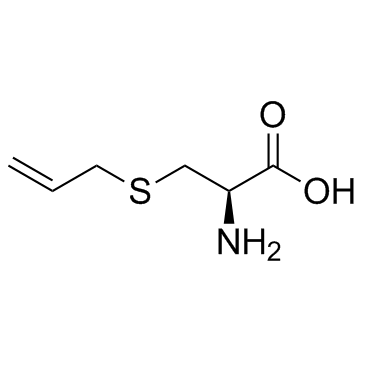
S-烯丙基-L-半胱氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | S-烯丙基-L-半胱氨酸 | 英文名 | S-Allyl-L-cysteine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 21593-77-1 | 分子量 | 161.222 | |
| 密度 | 1.191 | 沸点 | 300 ºC | |
| 分子式 | C6H11NO2S | 熔点 | 235-236 ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 135 ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Berberine and S allyl cysteine mediated amelioration of DEN+CCl4 induced hepatocarcinoma.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(1) , 219-44, (2014) Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) have been used as initiator and promoter respectively to establish an animal model for investigating molecular events appear to be involved in development of liver cancer. Use of herbal medicine in ther... |
|
|
The "aged garlic extract:" (AGE) and one of its active ingredients S-allyl-L-cysteine (SAC) as potential preventive and therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Curr. Med. Chem. 18 , 3306-3313, (2011) Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the older people and 7(th) leading cause of death in the United States. Deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques, hyperphosphorylation of microtubule associated protein tau (MAPT), neuroinflammati... |
|
|
S-allyl-L-cysteine and isoliquiritigenin improve mitochondrial function in cellular models of oxidative and nitrosative stress.
Food Chem. 194 , 843-8, (2015) Oxidative and nitrosative stress resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction are an early event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a key transcription factor and regulator of the cellular response... |
|
|
S-allyl cysteine in combination with clotrimazole downregulates Fas induced apoptotic events in erythrocytes of mice exposed to lead.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1820(1) , 9-23, (2012) Chronic lead (Pb(2+)) exposure leads to the reduced lifespan of erythrocytes. Oxidative stress and K(+) loss accelerate Fas translocation into lipid raft microdomains inducing Fas mediated death signaling in these erythrocytes. Pathophysiological-based therap... |
|
|
Effects of s-allyl-L-cysteine on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the mouse dentate gyrus.
J. Vet. Med. Sci. 73 , 1071-1075, (2011) In this study, we investigated the effects of S-allyl-L-cysteine (SAC), a major sulfur-containing compound present in garlic, on Ki67- and doublecortin (DCX)-positive cells, which were used as a marker for cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation, re... |
|
|
The effects and underlying mechanisms of S-allyl l-cysteine treatment of the retina after ischemia/reperfusion.
J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 28(2) , 110-7, (2012) Retinal ischemia-associated ocular disorders are vision-threatening. The aim of the present study was to examine whether S-allyl l-cysteine (SAC) is able to protect against retina ischemia/reperfusion injury.In vivo, retinal ischemia in the rat was induced by... |
|
|
High temperature- and high pressure-processed garlic improves lipid profiles in rats fed high cholesterol diets.
J. Med. Food 15(5) , 435-40, (2012) Garlic protects against degenerative diseases such as hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular diseases. However, raw garlic has a strong pungency, which is unpleasant. In this study, we examined the effect of high temperature/high pressure-processed garlic on plasm... |
|
|
S-allylcysteine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells.
Mol. Med. Report. 5(2) , 439-43, (2012) To increase the use of phytochemical supplements as chemoprevention or adjuvant drugs in cancer treatment, it is necessary to verify their biological effects and correlative mechanisms. Recently, S-allylcysteine (SAC) was identified as a potent compound deriv... |
|
|
S-Allylcysteine, a garlic compound, increases ABCA1 expression in human THP-1 macrophages.
Phytother Res. 27(3) , 357-61, (2013) ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) is a key mediator of cholesterol efflux to apoA-I in lipid-loaded macrophages, which is the first step of reverse cholesterol transport in vivo and a critical step in preventing atherosclerosis. Enhanced ABCA1 expre... |
|
|
Effect of S-allylcysteine, a sulphur containing amino acid on iron metabolism in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.
J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 27(2) , 143-7, (2013) It is suggested that iron may play a role in the pathogenesis of diabetes. Iron is not only chaperoned through its essential functional pathways, but it also causes damage to biological systems by catalyzing the production of reactive oxygen species. So, the ... |