S-Allylcysteine, a garlic compound, increases ABCA1 expression in human THP-1 macrophages.
Zahra Malekpour-Dehkordi, Ebrahim Javadi, Mahmood Doosti, Maliheh Paknejad, Mitra Nourbakhsh, Narguess Yassa, Siavash Gerayesh-Nejad, Ramin Heshmat
文献索引:Phytother Res. 27(3) , 357-61, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) is a key mediator of cholesterol efflux to apoA-I in lipid-loaded macrophages, which is the first step of reverse cholesterol transport in vivo and a critical step in preventing atherosclerosis. Enhanced ABCA1 expression may inhibit foam cell formation and consequently reduce atherogenic risk. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of S-allylcysteine (SAC), the most abundant organosulfur compound in aged garlic extract, on the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in human THP-1 macrophages. The human monocyte THP-1 cells were differentiated to macrophage cells in the presence of phorbol 12-myristate13-acetate (PMA). Macrophage cells were then treated with different concentrations (10, 20 and 40 mM) of SAC for 24 h. Total RNA of treated macrophages was extracted and analyzed with real-time RT-PCR. ABCA1 protein expression was also analyzed with western blotting. Results showed that SAC increased the ABCA1 mRNA (1.82-, 2.07- and 2.23-fold) and protein (1.37-, 1.55- and 2.08-fold) expression in macrophage THP-1 cells compared with control (untreated cells). Results suggested that SAC can increase ABCA1 expression in macrophages and may be beneficial in promoting reverse cholesterol efflux.Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
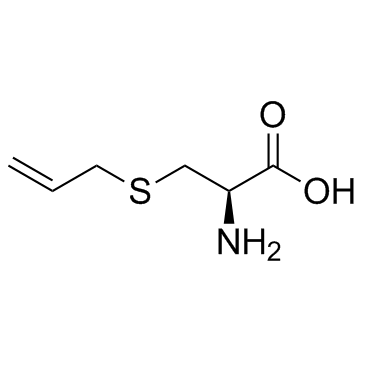 |
S-烯丙基-L-半胱氨酸
CAS:21593-77-1 |
C6H11NO2S |
|
Berberine and S allyl cysteine mediated amelioration of DEN+...
2014-01-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(1) , 219-44, (2014)] |
|
The "aged garlic extract:" (AGE) and one of its active ingre...
2011-01-01 [Curr. Med. Chem. 18 , 3306-3313, (2011)] |
|
S-allyl-L-cysteine and isoliquiritigenin improve mitochondri...
2016-03-01 [Food Chem. 194 , 843-8, (2015)] |
|
S-allyl cysteine in combination with clotrimazole downregula...
2012-01-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1820(1) , 9-23, (2012)] |
|
Effects of s-allyl-L-cysteine on cell proliferation and neur...
2011-08-01 [J. Vet. Med. Sci. 73 , 1071-1075, (2011)] |