3,5-二甲氧基苯酚
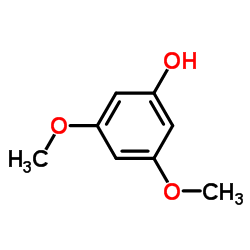
3,5-二甲氧基苯酚结构式

|
常用名 | 3,5-二甲氧基苯酚 | 英文名 | 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 500-99-2 | 分子量 | 154.163 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 294.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H10O3 | 熔点 | 40-43 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 78.3±0.0 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Importance of phenols structure on their activity as antinitrosating agents: A kinetic study.
J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 3(1) , 128-34, (2011) Nitrosative deamination of DNA bases induced by reaction with reactive nitrogen species (RNS) has been pointed out as a probable cause of mutagenesis. (Poly)phenols, present in many food items from the Mediterranean diet, are believed to possess antinitrosati... |
|
|
Fatal poisoning with Taxus baccata: quantification of paclitaxel (taxol A), 10-deacetyltaxol, baccatin III, 10-deacetylbaccatin III, cephalomannine (taxol B), and 3,5-dimethoxyphenol in body fluids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Anal. Toxicol. 36(1) , 36-43, (2012) This method development was to confirm the fatal ingestion of toxic yew plant material in postmortem samples (stomach content, urine, femoral blood, cardiac blood, bile, and brain tissue) collected from a 22-year-old man who committed suicide by ingesting yew... |
|
|
[3,5-dimethoxyfenol--marker intoxication with Taxus baccata].
Soud. Lek. 55(3) , 36-9, (2010) Autopsy findings of fatal intoxication with yew (Taxus baccata) are nonspecific. A presence of plant residues in the digestive tract can signalize yew intoxication. If yew decoction is consumed, plant residues are not found. In such a case the intoxication ca... |
|
|
Extracorporeal life support in a severe Taxus baccata poisoning.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 48(5) , 463-5, (2010) Yew (Taxus baccata) is a conifer known to be toxic since ancient times. Taxine A and taxine B, the toxic alkaloids of Taxus, block cardiac sodium and calcium channels causing nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory distress, coma, s... |
|
|
A comparative study of five fatal cases of Taxus poisoning.
Int. J. Legal Med. 121(5) , 417-22, (2007) The study presents five fatal cases of poisoning with Taxus spp., all of which were suicides of young people aged between 16 and 26 years. Yew leaves were consumed in four fatalities, whereas a mash from Taxus was ingested in one case. No relevant concentrati... |
|
|
Preliminary gas chromatography with mass spectrometry determination of 3,5-dimethoxyphenol in biological specimens as evidence of taxus poisoning.
J. Anal. Toxicol. 34(1) , 53-6, (2010) Taxus baccata is a widely distributed yew often associated with cases of fatal intoxication, which is related to the high amounts of cardiotoxic alkaloids, taxine A and taxine B, contained in its leaves. In this paper, a case of Taxus fatal poisoning, hypothe... |
|
|
Unusual pseudosubstrate specificity of a novel 3,5-dimethoxyphenol O-methyltransferase cloned from Ruta graveolens L.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 440(1) , 54-64, (2005) A cDNA was cloned from Ruta graveolens cells encoding a novel O-methyltransferase (OMT) with high similarity to orcinol or chavicol/eugenol OMTs, but containing a serine-rich N-terminus and a 13 amino acid insertion between motifs IV and V. Expression in Esch... |
|
|
Suicidal yew leave ingestion--phloroglucindimethylether (3,5-dimethoxyphenol) as a marker for poisoning from Taxus baccata.
Int. J. Legal Med. 106(1) , 45-50, (1993) In a case of suicide in a depressive 19-year-old man with considerable ingestion of new leaves, resorption of yew ingredients could be demonstrated. The main substance could be identified as 3,5-dimethoxyphenol, the aglycone of taxicatine, which is a typical ... |
|
|
Modern analytical procedures for the determination of taxus alkaloids in biological material.
Int. J. Legal Med. 122(4) , 357-8, (2008)
|
|
|
Iron porphyrin phenoxides: models for some hemoglobin mutants. Ainscough E_W, et al.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100(24) , 7585-7591, (1978)
|