3,5-Dimethoxyphenol
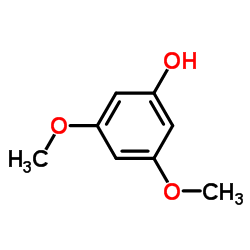
3,5-Dimethoxyphenol structure
|
Common Name | 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 500-99-2 | Molecular Weight | 154.163 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 294.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O3 | Melting Point | 40-43 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 78.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol3,5-Dimethoxyphenol is a toxin metabolite, found in human consuming yew leaves[1]. |
| Name | 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol is a toxin metabolite, found in human consuming yew leaves[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 294.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 40-43 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.163 |
| Flash Point | 78.3±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 154.062988 |
| PSA | 38.69000 |
| LogP | 1.43 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.523 |
| InChIKey | XQDNFAMOIPNVES-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(O)cc(OC)c1 |
| Storage condition | Store in dark! |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29095090 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2909500000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2909500000 ether-phenols, ether-alcohol-phenols and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Importance of phenols structure on their activity as antinitrosating agents: A kinetic study.
J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 3(1) , 128-34, (2011) Nitrosative deamination of DNA bases induced by reaction with reactive nitrogen species (RNS) has been pointed out as a probable cause of mutagenesis. (Poly)phenols, present in many food items from th... |
|
|
Fatal poisoning with Taxus baccata: quantification of paclitaxel (taxol A), 10-deacetyltaxol, baccatin III, 10-deacetylbaccatin III, cephalomannine (taxol B), and 3,5-dimethoxyphenol in body fluids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Anal. Toxicol. 36(1) , 36-43, (2012) This method development was to confirm the fatal ingestion of toxic yew plant material in postmortem samples (stomach content, urine, femoral blood, cardiac blood, bile, and brain tissue) collected fr... |
|
|
[3,5-dimethoxyfenol--marker intoxication with Taxus baccata].
Soud. Lek. 55(3) , 36-9, (2010) Autopsy findings of fatal intoxication with yew (Taxus baccata) are nonspecific. A presence of plant residues in the digestive tract can signalize yew intoxication. If yew decoction is consumed, plant... |
| Taxicatigenin |
| 1-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzene |
| phloroglucinol dimethylether |
| EINECS 207-917-7 |
| Phenol,5-dimethoxy |
| Phloroglucinol Dimethyl Ether |
| 3,5-dimethoxy-phenol |
| 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol |
| Phenol,3,5-dimethoxy |
| O,O-dimethyl-phloroglucinol |
| Phenol, 3,5-dimethoxy- |
| MFCD00008388 |
| O-dimethylphloroglucinol |
 CAS#:621-23-8
CAS#:621-23-8 CAS#:108-73-6
CAS#:108-73-6 CAS#:77-78-1
CAS#:77-78-1 CAS#:155935-98-1
CAS#:155935-98-1 CAS#:74-88-4
CAS#:74-88-4 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:1376626-55-9
CAS#:1376626-55-9 CAS#:365564-07-4
CAS#:365564-07-4 CAS#:34967-24-3
CAS#:34967-24-3 CAS#:487-06-9
CAS#:487-06-9 CAS#:144688-05-1
CAS#:144688-05-1 CAS#:14639-73-7
CAS#:14639-73-7 CAS#:90-24-4
CAS#:90-24-4 CAS#:13246-14-5
CAS#:13246-14-5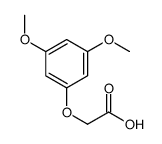 CAS#:19728-23-5
CAS#:19728-23-5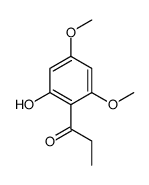 CAS#:2215-82-9
CAS#:2215-82-9 CAS#:18799-43-4
CAS#:18799-43-4 CAS#:18113-21-8
CAS#:18113-21-8
