Acetyl chloride
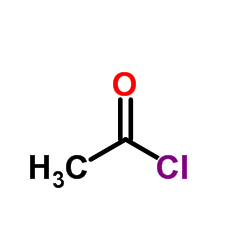
Acetyl chloride structure
|
Common Name | Acetyl chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-36-5 | Molecular Weight | 78.498 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 46.0±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3ClO | Melting Point | -112 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 4.4±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | acetyl chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 46.0±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -112 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3ClO |
| Molecular Weight | 78.498 |
| Flash Point | 4.4±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 77.987244 |
| PSA | 17.07000 |
| LogP | 0.46 |
| Vapour density | 2.7 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 341.6±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.379 |
| InChIKey | WETWJCDKMRHUPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)Cl |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302-H314 |
| Supplemental HS | Reacts violently with water. |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R14;R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S9-S16-S26-S45-S1/2 |
| RIDADR | UN 1717 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | AO6390000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| HS Code | 2915900090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2915900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2915900090 other saturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Epitope mapping of the 2009 pandemic and the A/Brisbane/59/2007 seasonal (H1N1) influenza virus haemagglutinins using mAbs and escape mutants.
J. Gen. Virol. 95(Pt 11) , 2377-89, (2014) mAbs constitute an important biological tool for influenza virus haemagglutinin (HA) epitope mapping through the generation of escape mutants, which could provide insights into immune evasion mechanis... |
|
|
Limited effect of recombinant human mannose-binding lectin on the infection of novel influenza A (H7N9) virus in vitro.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 458(1) , 77-81, (2015) Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), a pattern-recognition molecule in serum, recognizes specific hexose sugars rich in mannose and N-acetylglucosamine on bacterium, yeasts, viruses as well as apoptotic cell... |
|
|
Remarkably regioselective deacylation of cellulose esters using tetraalkylammonium salts of the strongly basic hydroxide ion.
Carbohydr. Polym. 111 , 25-32, (2014) Tetraalkylammonium hydroxides have been found to mediate regioselective deacylation of cellulose esters. This deacylation surprisingly shows substantial selectivity for the removal of the acyl groups ... |
| EINECS 200-865-6 |
| Ethanoic acid chloride |
| 1-Chloroethanone |
| Ethanoylcholride |
| MFCD00000719 |
| acetic acid chloride |
| ACETYLCLORIDE |
| CH3COCl |
| acetylchloride313 |
| Acetic chloride |
| Acetylchlorid |
| Acetyl chloride |
| ethanoyl chloride |
| acid chloride |
| acetochlor [ANSI, WSSA] |
 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7 CAS#:14243-64-2
CAS#:14243-64-2 CAS#:506-96-7
CAS#:506-96-7 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7 CAS#:629-19-6
CAS#:629-19-6 CAS#:10436-57-4
CAS#:10436-57-4 CAS#:186581-53-3
CAS#:186581-53-3 CAS#:79-37-8
CAS#:79-37-8 CAS#:32362-99-5
CAS#:32362-99-5![1-[4-[4-[4-(4-acetylphenoxy)phenyl]phenoxy]phenyl]ethanone structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/440/106991-88-2.png) CAS#:106991-88-2
CAS#:106991-88-2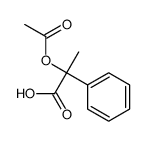 CAS#:10487-92-0
CAS#:10487-92-0 CAS#:104729-89-7
CAS#:104729-89-7 CAS#:105400-12-2
CAS#:105400-12-2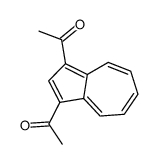 CAS#:10487-55-5
CAS#:10487-55-5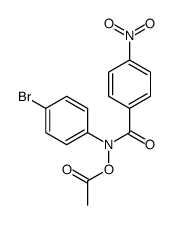 CAS#:108009-19-4
CAS#:108009-19-4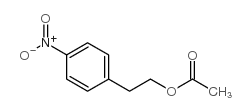 CAS#:104-30-3
CAS#:104-30-3 CAS#:106738-27-6
CAS#:106738-27-6 CAS#:1078-97-3
CAS#:1078-97-3 CAS#:10500-11-5
CAS#:10500-11-5
