monochloroethane
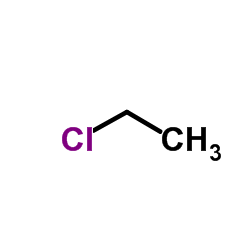
monochloroethane structure
|
Common Name | monochloroethane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-00-3 | Molecular Weight | 64.514 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 12.7±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5Cl | Melting Point | −139 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | -56.7±2.8 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | chloroethane |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 12.7±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | −139 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5Cl |
| Molecular Weight | 64.514 |
| Flash Point | -56.7±2.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 64.007980 |
| LogP | 1.50 |
| Vapour density | 2.22 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 1169.9±0.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.362 |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable - may form explosive mixtures with air. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alkali metals and their alloys. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H315-H351 |
| Supplemental HS | May form explosive peroxides., Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness or cracking. |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P281 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
| Hazard Codes | F+:Extremelyflammable;Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R12;R40;R52/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S9-S16-S33-S36/37-S61-S45-S7-S29-S36/37/39-S26-S53 |
| RIDADR | UN 1993 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | KH7525000 |
| Hazard Class | 2.1 |
| HS Code | 2903110000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2903110000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2903110000 chloroethane。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。Lowest tariff:5.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
QSPR modeling of octanol/water partition coefficient for vitamins by optimal descriptors calculated with SMILES.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43 , 714-40, (2008) Simplified molecular input line entry system (SMILES) has been utilized in constructing quantitative structure-property relationships (QSPR) for octanol/water partition coefficient of vitamins and org... |
|
|
Identification of Dehalobacter reductive dehalogenases that catalyse dechlorination of chloroform, 1,1,1-trichloroethane and 1,1-dichloroethane.
Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 368(1616) , 20120318, (2013) Two novel reductive dehalogenases (RDases) that are highly similar to each other but catalyse distinct dechlorination reactions were identified from Dehalobacter-containing mixed cultures. These two R... |
|
|
Development of QSAR models for predicting hepatocarcinogenic toxicity of chemicals.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44 , 3658-64, (2009) A dataset comprising 55 chemicals with hepatocarcinogenic potency indices was collected from the Carcinogenic Potency Database with the aim of developing QSAR models enabling prediction of the above u... |
| ethyl cerotate |
| Hexacosansaeure-aethylester |
| monochloroethane |
| 1-CHLORO-ETHANE |
| hydrochloric ether |
| Ethane, chloro- |
| Ethylhexacosanoat |
| Chloroethane |
| ethyl chloride |
| 1-ethyl chloride |
| mono-chloroethane |
| hexacosanoic acid ethyl ester |
| MFCD00000961 |
| ETHYL HEXACOSANATE |
| EINECS 200-830-5 |
 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:87463-00-1
CAS#:87463-00-1 CAS#:74-96-4
CAS#:74-96-4 CAS#:141-78-6
CAS#:141-78-6 CAS#:65039-09-0
CAS#:65039-09-0 CAS#:60-29-7
CAS#:60-29-7 CAS#:103-80-0
CAS#:103-80-0 CAS#:93-89-0
CAS#:93-89-0 CAS#:75-03-6
CAS#:75-03-6 CAS#:105-93-1
CAS#:105-93-1![1,2-Ethanediamine,N1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-N1,N2,N2-triethyl- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/466/24426-21-9.png) CAS#:24426-21-9
CAS#:24426-21-9![N-ethyl-N'-[2-(ethylamino)ethyl]ethane-1,2-diamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/209/4432-87-5.png) CAS#:4432-87-5
CAS#:4432-87-5![N'-[2-(ethylamino)ethyl]ethane-1,2-diamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/012/137554-10-0.png) CAS#:137554-10-0
CAS#:137554-10-0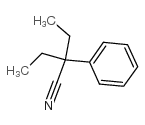 CAS#:5336-57-2
CAS#:5336-57-2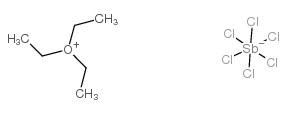 CAS#:3264-67-3
CAS#:3264-67-3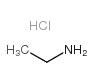 CAS#:557-66-4
CAS#:557-66-4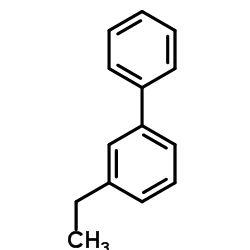 CAS#:5668-93-9
CAS#:5668-93-9 CAS#:699-91-2
CAS#:699-91-2 CAS#:488-17-5
CAS#:488-17-5