Carnosol

Carnosol structure
|
Common Name | Carnosol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5957-80-2 | Molecular Weight | 330.418 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 524.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H26O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 187.0±23.6 °C | |
Use of CarnosolCarnosol is a potent Ribosomal S6 Kinase (RSK2) inhibitor that could be useful for treating gastric cancer, with an IC50 of ~5.5 μM. |
| Name | carnosol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carnosol is a potent Ribosomal S6 Kinase (RSK2) inhibitor that could be useful for treating gastric cancer, with an IC50 of ~5.5 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 5.5 μM (RSK2)[1]. |
| In Vitro | It is showed that carnosol has no cytotoxic effects on GES1 cells and 10 μM carnosol strongly suppresses RSK2 activity, but has little effect on any other kinase. Carnosol exerts strong dose-dependent inhibitory effects against RSK2 autophosphorylation and phosphorylation of its substrate ATF1[1]. |
| In Vivo | Results indicate that Carnosol significantly decreaseS the volume and weight of gastric tumors relative to the vehicle-treated group. Additionally, mice tolerate treatment with carnosol without significant loss of body weight similar to the vehicle-treated group. The phosphorylation of CREB, a direct downstream protein of RSK2, Is strongly inhibited in the carnosol-treated group but the expression of total CREB is relatively unchanged[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Mice are orally administrated Carnosol at 100 mg/kg or vehicle 5 times a week over a period of 31 days[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 524.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H26O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 330.418 |
| Flash Point | 187.0±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 330.183105 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 3.71 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.607 |
| InChIKey | XUSYGBPHQBWGAD-PJSUUKDQSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)c1cc2c(c(O)c1O)C13CCCC(C)(C)C1CC2OC3=O |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
Calcium and α-tocopherol suppress cured-meat promotion of chemically induced colon carcinogenesis in rats and reduce associated biomarkers in human volunteers.
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 98(5) , 1255-62, (2013) Processed meat intake has been associated with increased colorectal cancer risk. We have shown that cured meat promotes carcinogen-induced preneoplastic lesions and increases specific biomarkers in th... |
|
|
Degradation study of carnosic acid, carnosol, rosmarinic acid, and rosemary extract (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) assessed using HPLC.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(36) , 9305-14, (2012) Rosemary, whose major caffeoyl-derived and diterpenoid ingredients are rosmarinic acid, carnosol, and carnosic acid, is an important source of natural antioxidants and is being recognized increasingly... |
|
|
Relevance of carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmarinic acid concentrations in the in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rosmarinus officinalis (L.) methanolic extracts.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(38) , 9603-8, (2012) The importance of the diterpenic and rosmarinic acid content in the biological activities of rosemary extracts has been studied previously, but how the relationship between the concentration of these ... |
| (7β)-11,12-Dihydroxy-7,20-epoxyabieta-8,11,13-trien-20-one |
| (7β)-11,12-Dihydroxy-7,20-epoxyabieta-8(14),9(11),12-trien-20-one |
| 2H-9,4a-(Epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, 1,3,4,9,10,10a-hexahydro-5,6-dihydroxy-1,1-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl)-, (4aR,9S,10aS)- |
| Carnosol |
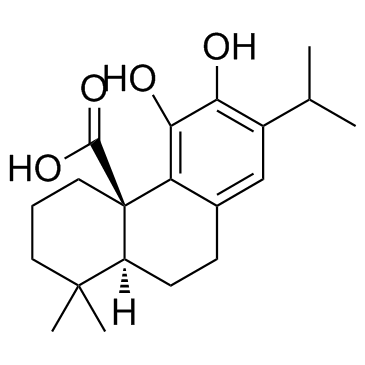 CAS#:3650-09-7
CAS#:3650-09-7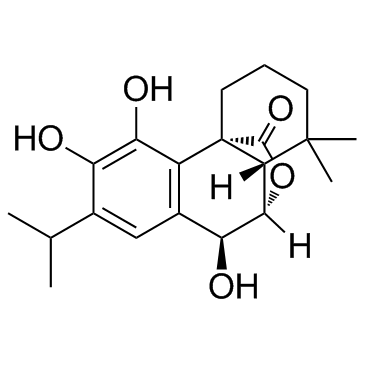 CAS#:80225-53-2
CAS#:80225-53-2
