S-Phenyl-L-cysteine
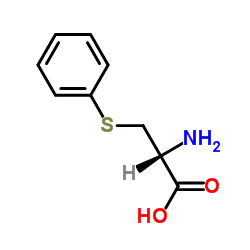
S-Phenyl-L-cysteine structure
|
Common Name | S-Phenyl-L-cysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34317-61-8 | Molecular Weight | 197.25 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 361.5±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO2S | Melting Point | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 172.4±26.5 °C | |
Use of S-Phenyl-L-cysteineS-Phenylcysteine is acysteine derivatives. |
| Name | (2R)-2-amino-3-phenylsulfanylpropanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | S-Phenylcysteine is acysteine derivatives. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 361.5±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 197.25 |
| Flash Point | 172.4±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 197.051056 |
| PSA | 88.62000 |
| LogP | 1.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.624 |
| InChIKey | XYUBQWNJDIAEES-QMMMGPOBSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(CSc1ccccc1)C(=O)O |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Comparative study on the bioactivation mechanisms and cytotoxicity of Te-phenyl-L-tellurocysteine, Se-phenyl-L-selenocysteine, and S-phenyl-L-cysteine.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15(12) , 1610-8, (2002) Tellurium compounds are effective antioxidants and chemoprotectors, even more active than their selenium and sulfur analogues. In addition to these properties, some selenium compounds, such as selenoc... |
|
|
Biomarkers of human exposure to benzene.
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 40(2-3) , 377-86, (1993) Three biomarkers for benzene exposure were developed. The first biomarker, muconic acid in urine, results from the ring opening of a benzene metabolite. A gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy (GC/MS) ... |
|
|
S-phenylcysteine formation in hemoglobin as a biological exposure index to benzene.
Arch. Toxicol. 66(5) , 303-9, (1992) Benzene is metabolized to intermediates that bind to hemoglobin, forming adducts. These hemoglobin adducts may be usable as biomarkers of exposure. In this paper, we describe the development of a gas ... |
| MFCD01318758 |
| (2R)-2-amino-3-phenylthiopropanoic acid |
| S-phenyl-L-cysteine |
| L-Cysteine,S-phenyl |
| (L)-2-amino-3-(phenylthio)propanoic acid |
| (R)-S-Phenylcystein |
| Cysteine, S-phenyl- |
| S-Phenylcysteine |
| 3-(Phenylthio)-L-Alanine,4-Thia-L-homophenylalanine |
| QVYZ1SR &&L or R Form |
| 4-Thia-L-homophenylalanine |
| 3-Phenylcysteine |
| L-S-phenylcysteine |
| (R)-S-phenylcysteine |
| S-Ph-L-cysteine |
| (R)-2-Amino-3-(phenylthio)propanoic acid |
| 3-(Phenylthio)-L-Alanine |
 CAS#:56-45-1
CAS#:56-45-1 CAS#:108-98-5
CAS#:108-98-5 CAS#:2731-73-9
CAS#:2731-73-9 CAS#:52-90-4
CAS#:52-90-4 CAS#:1483-72-3
CAS#:1483-72-3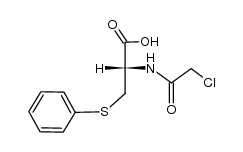 CAS#:121704-26-5
CAS#:121704-26-5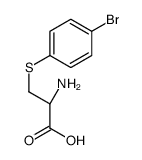 CAS#:68724-10-7
CAS#:68724-10-7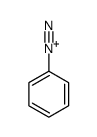 CAS#:2684-02-8
CAS#:2684-02-8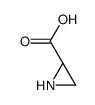 CAS#:1758-77-6
CAS#:1758-77-6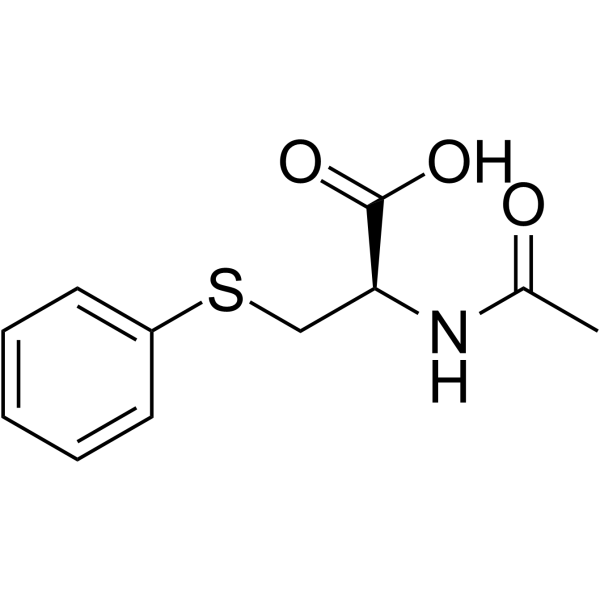 CAS#:4775-80-8
CAS#:4775-80-8 CAS#:75-07-0
CAS#:75-07-0 CAS#:302-72-7
CAS#:302-72-7 CAS#:882-33-7
CAS#:882-33-7 CAS#:66303-55-7
CAS#:66303-55-7 CAS#:82611-65-2
CAS#:82611-65-2
