DL-Alanine

DL-Alanine structure
|
Common Name | DL-Alanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 302-72-7 | Molecular Weight | 89.093 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 212.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 | Melting Point | 272-275ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 82.6±22.6 °C | |
Use of DL-AlanineDL-alanine, an amino acid, is the racemic compound of L- and D-alanine. DL-alanine is employed both as a reducing and a capping agent, used with silver nitrate aqueous solutions for the production of nanoparticles. DL-alanine can be used for the research of transition metals chelation, such as Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(11). DL-alanine, a sweetener, is classed together with glycine, and sodium saccharin. DL-alanine plays a key role in the glucose-alanine cycle between tissues and liver[1][2][3][4][5][6]. |
| Name | alanine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-alanine, an amino acid, is the racemic compound of L- and D-alanine. DL-alanine is employed both as a reducing and a capping agent, used with silver nitrate aqueous solutions for the production of nanoparticles. DL-alanine can be used for the research of transition metals chelation, such as Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(11). DL-alanine, a sweetener, is classed together with glycine, and sodium saccharin. DL-alanine plays a key role in the glucose-alanine cycle between tissues and liver[1][2][3][4][5][6]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[6]. Tapper DN, et al. Taste stimuli: a behavioral categorization. Science. 1968 Aug 16;161(3842):708-10. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 212.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 272-275ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 89.093 |
| Flash Point | 82.6±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 89.047676 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | -0.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.460 |
| InChIKey | QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(N)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 156 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AY2980000 |
| HS Code | 2936240000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) protease: a chymotrypsin-like enzyme that processes both non-structural (pORF1) and capsid (pORF2) protein.
J. Gen. Virol. 95(Pt 8) , 1689-700, (2014) Hepatitis E virus (HEV), a major cause of acute viral hepatitis across the world, is a non-enveloped, plus-strand RNA virus. Its genome codes three proteins, pORF1 (multifunctional polyprotein), pORF2... |
|
|
Rad23 interaction with the proteasome is regulated by phosphorylation of its ubiquitin-like (UbL) domain.
J. Mol. Biol. 426(24) , 4049-60, (2014) Rad23 was identified as a DNA repair protein, although a role in protein degradation has been described. The protein degradation function of Rad23 contributes to cell cycle progression, stress respons... |
|
|
Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor gamma extracellular domain (sPTPRG) as a natural soluble protein in plasma.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0119110, (2015) PTPRG is a widely expressed protein tyrosine phosphatase present in various isoforms. Peptides from its extracellular domain have been detected in plasma by proteomic techniques. We aim at characteriz... |
| (R,S)-Alanine |
| (±)-Alanine |
| Propanoic acid, 2-amino- |
| (±)-2-Aminopropionic acid |
| 2-amino-propanoic acid |
| DL-2-aminopropionic acid |
| α-Aminopropanoic acid |
| 2-Aminopropanoic acid |
| ZY1&VQ |
| Alanine,DL |
| EINECS 206-126-4 |
| Alanine |
| α-Aminopropionic acid |
| d,l-alanine |
| Alanine, DL- |
| UNII:1FU7983T0U |
| α-Alanine |
| 2-Aminopropionic Acid |
| DL-α-Aminopropionic acid |
| MFCD00064408 |
| H-DL-Ala-OH |
| DL-2-Aminopropanoic acid |
| DL-α-Alanine |
| DL-Aminopropanoic acid |
| Methyl glycine |
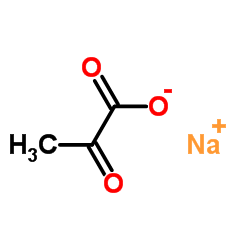 CAS#:113-24-6
CAS#:113-24-6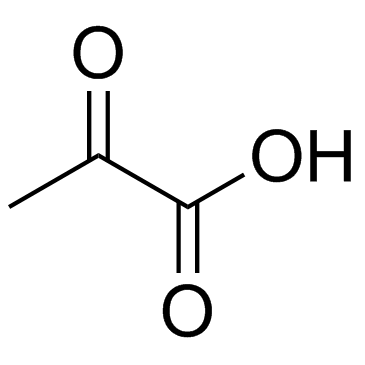 CAS#:127-17-3
CAS#:127-17-3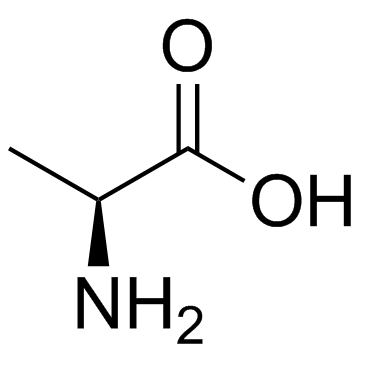 CAS#:56-41-7
CAS#:56-41-7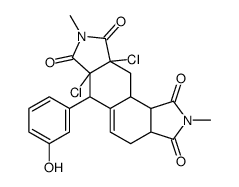 CAS#:6060-58-8
CAS#:6060-58-8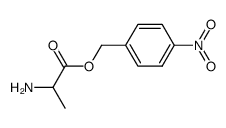 CAS#:7352-65-0
CAS#:7352-65-0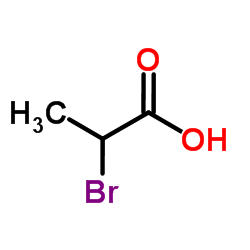 CAS#:598-72-1
CAS#:598-72-1 CAS#:143-33-9
CAS#:143-33-9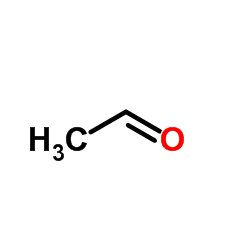 CAS#:75-07-0
CAS#:75-07-0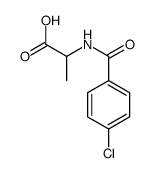 CAS#:108462-95-9
CAS#:108462-95-9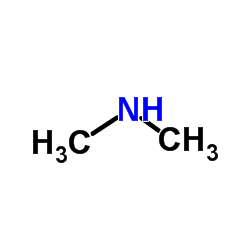 CAS#:124-40-3
CAS#:124-40-3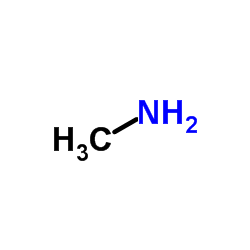 CAS#:74-89-5
CAS#:74-89-5 CAS#:75-50-3
CAS#:75-50-3 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9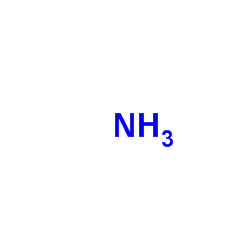 CAS#:7664-41-7
CAS#:7664-41-7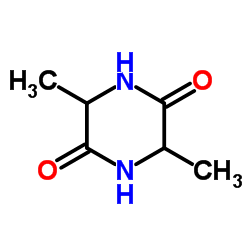 CAS#:5625-46-7
CAS#:5625-46-7 CAS#:529-96-4
CAS#:529-96-4 CAS#:598-78-7
CAS#:598-78-7
