S-Phenylmercapturic Acid
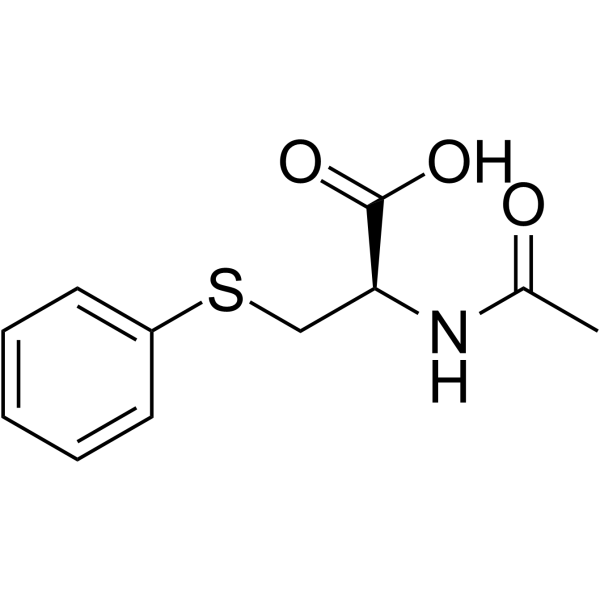
S-Phenylmercapturic Acid structure
|
Common Name | S-Phenylmercapturic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4775-80-8 | Molecular Weight | 211.28100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 494.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13NO2S | Melting Point | 110-112ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 252.9ºC | |
Use of S-Phenylmercapturic AcidS-Phenylmercapturic acid, a metabolite of benzene, can be used as a biomarker, identified by GC, HPLC (UV or fluorescence detection), GC-MS, LC-MS/MS or immunoassay[1]. |
| Name | S-Phenylmercapturic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | S-Phenylmercapturic acid, a metabolite of benzene, can be used as a biomarker, identified by GC, HPLC (UV or fluorescence detection), GC-MS, LC-MS/MS or immunoassay[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 494.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 110-112ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13NO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 211.28100 |
| Flash Point | 252.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 211.06700 |
| PSA | 74.63000 |
| LogP | 1.84220 |
| Storage condition | -20?C Freezer |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~27% 
S-Phenylmercapt... CAS#:4775-80-8 |
| Literature: Hickman; Christie; Guy; White Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1985 , vol. 38, # 6 p. 899 - 904 |
|
~% 
S-Phenylmercapt... CAS#:4775-80-8 |
| Literature: Zbarsky; Young Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1943 , vol. 151, p. 211,212 |
|
~% 
S-Phenylmercapt... CAS#:4775-80-8 |
| Literature: Zbarsky; Young Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1943 , vol. 151, p. 211,212 |
|
~% 
S-Phenylmercapt... CAS#:4775-80-8 |
| Literature: Zbarsky; Young Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1943 , vol. 151, p. 211,212 |
|
~% 
S-Phenylmercapt... CAS#:4775-80-8 |
| Literature: Zbarsky; Young Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1943 , vol. 151, p. 211,212 |
|
~% 
S-Phenylmercapt... CAS#:4775-80-8 |
| Literature: Baumann; Preusse Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift fuer Physiologische Chemie, 1881 , vol. 5, p. 337 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Influence of genetic polymorphism on t,t-MA/S-PMA ratio in 301 benzene exposed subjects.
Toxicol. Lett. 231(2) , 205-12, (2014) This study investigated the effect of polymorphic genes GSTT1, GSTM1, GSTA1, EHPX1, NQO1, CYP2E1, CYP1A and MPO on the urinary concentrations and ratio (R) of the benzene metabolites trans,trans-mucon... |
|
|
Metabolic polymorphisms and biomarkers of effect in the biomonitoring of occupational exposure to low-levels of benzene: state of the art.
Toxicol. Lett. 231(2) , 194-204, (2014) Current levels of occupational exposure to benzene, a genotoxic human carcinogen, in Western countries are reduced by two-three orders of magnitude (from ppm to ppb) as compared to the past. However, ... |
|
|
Urinary trans, trans-muconic acid and S-phenylmercapturic acid are indicative of exposure to urban benzene pollution during childhood.
Sci. Total Environ. 435-436 , 115-23, (2012) The aims of the study were to evaluate the feasibility of urinary trans, trans-muconic acid (u-t,t-MA) and urinary S-phenylmercapturic acid (u-SPMA) as markers of exposure to urban benzene pollution f... |
| s-phenylmercapturic acid |



 CAS#:5437-52-5
CAS#:5437-52-5 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7