N-Acetyl-D-lactosamine
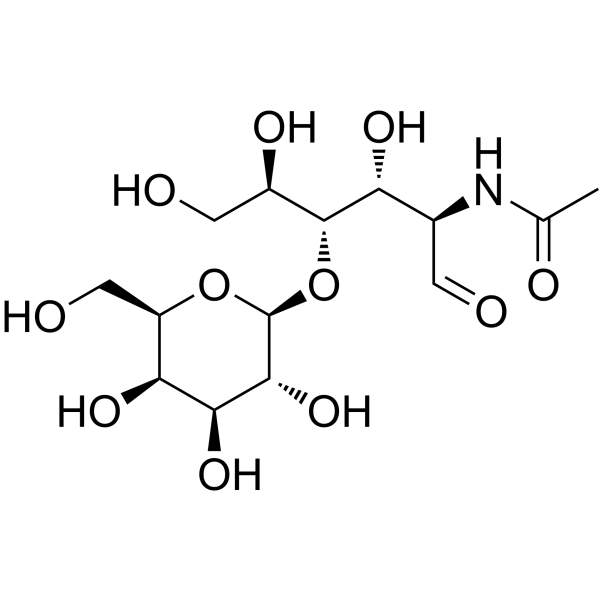
N-Acetyl-D-lactosamine structure
|
Common Name | N-Acetyl-D-lactosamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 32181-59-2 | Molecular Weight | 383.34800 | |
| Density | 1.64 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 805.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H25NO11 | Melting Point | 191-192ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 441ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of N-Acetyl-D-lactosamineN-Acetyllactosamine (LacNAc), a nitrogen-containing disaccharide, is an important component of various oligosaccharides such as glycoproteins and sialyl Lewis X. N-Acetyllactosamine can be used as the starting material for the synthesis of various oligosaccharides. N-Acetyllactosamine has prebiotic effects[1][2]. |
| Name | N-acetyllactosamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Acetyllactosamine (LacNAc), a nitrogen-containing disaccharide, is an important component of various oligosaccharides such as glycoproteins and sialyl Lewis X. N-Acetyllactosamine can be used as the starting material for the synthesis of various oligosaccharides. N-Acetyllactosamine has prebiotic effects[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.64 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 805.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 191-192ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C14H25NO11 |
| Molecular Weight | 383.34800 |
| Flash Point | 441ºC |
| Exact Mass | 383.14300 |
| PSA | 198.40000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.623 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~9% 
N-Acetyl-D-lact... CAS#:32181-59-2 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 68, # 9 p. 2141 - 2145 |
|
~% 
N-Acetyl-D-lact... CAS#:32181-59-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Biological Chemistry, , vol. 217, p. 79,81 Archives of Biochemistry, , vol. 54, p. 398,402 |
|
~% 
N-Acetyl-D-lact... CAS#:32181-59-2 |
| Literature: Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, , vol. 52, p. 145,146 |
|
~% 
N-Acetyl-D-lact... CAS#:32181-59-2 |
| Literature: Chemische Berichte, , vol. 87, p. 1547,1551 |
|
Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Joint Protection in Collagen-Induced Arthritis after Treatment with IQ-1S, a Selective c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitor.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 353 , 505-16, (2015) c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) participate in many physiologic and pathologic processes, including inflammatory diseases. We recently synthesized the sodium salt of IQ-1S (11H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin... |
|
|
BAFF activation of the ERK5 MAP kinase pathway regulates B cell survival.
J. Exp. Med. 212 , 883-92, (2015) B cell activating factor (BAFF) stimulation of the BAFF receptor (BAFF-R) is essential for the homeostatic survival of mature B cells. Earlier in vitro experiments with inhibitors that block MEK 1 and... |
|
|
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Infection and Sensing Capacity during Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection.
J. Virol. 89 , 6918-27, (2015) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in humans and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in macaques (MAC) lead to chronic inflammation and AIDS. Natural hosts, such as African green monkeys (AGM) and soo... |
| N-Acetyl-D-lactosamine |
| N-Acetyllactosamine |
| N-ACETYLLACTOSAMINE |


![2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[(5Z)-1,2,4-trihydroxy-5,6-bis(phenylhydrazinylidene)hexan-3-yl]oxy-oxane-3,4,5-triol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/367/4746-17-2.png)

