Benfotiamine
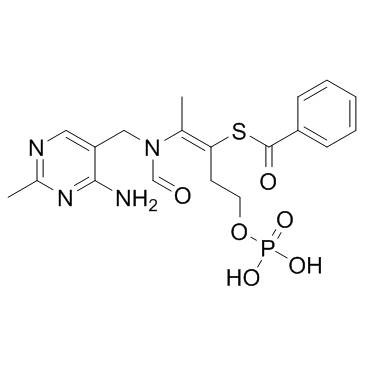
Benfotiamine structure
|
Common Name | Benfotiamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22457-89-2 | Molecular Weight | 466.448 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 745.1±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N4O6PS | Melting Point | 165ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 404.4±35.7 °C | |
Use of BenfotiamineBenfotiamine is a synthetic S-acyl derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1); an antioxidant dietary supplement.IC50 value:Target: Benfotiamine, the lipid-soluble thiamine derivative used as a treatment for diabetic neuropathy, can inhibit three major pathways(the hexosamine pathway, the advanced glycation end product (AGE) formation pathway and the diacylglycerol (DAG)?protein kinase C (PKC) pathway)of hyperglycemic damage and prevent experimental diabetic retinopathy. Benfotiamine is a synthetic S-acyl derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1) for treating sciatica and other painful nerve conditions. More effective at increasing thiamin levels in blood and tissues than water-soluble salts like the previous vitamin B1. |
| Name | benfotiamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Benfotiamine is a synthetic S-acyl derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1); an antioxidant dietary supplement.IC50 value:Target: Benfotiamine, the lipid-soluble thiamine derivative used as a treatment for diabetic neuropathy, can inhibit three major pathways(the hexosamine pathway, the advanced glycation end product (AGE) formation pathway and the diacylglycerol (DAG)?protein kinase C (PKC) pathway)of hyperglycemic damage and prevent experimental diabetic retinopathy. Benfotiamine is a synthetic S-acyl derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1) for treating sciatica and other painful nerve conditions. More effective at increasing thiamin levels in blood and tissues than water-soluble salts like the previous vitamin B1. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[6]. Benfotiamine |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 745.1±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 165ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N4O6PS |
| Molecular Weight | 466.448 |
| Flash Point | 404.4±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 466.107605 |
| PSA | 191.05000 |
| LogP | 1.81 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.645 |
| InChIKey | BTNNPSLJPBRMLZ-GHRIWEEISA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=C(CCOP(=O)(O)O)SC(=O)c1ccccc1)N(C=O)Cc1cnc(C)nc1N |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
Benfotiamine, a synthetic S-acyl thiamine derivative, has different mechanisms of action and a different pharmacological profile than lipid-soluble thiamine disulfide derivatives.
BMC Pharmacol. 8 , 10, (2008) Lipid-soluble thiamine precursors have a much higher bioavailability than genuine thiamine and therefore are more suitable for therapeutic purposes. Benfotiamine (S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate), a... |
|
|
The detrimental effects of acute hyperglycemia on myocardial glucose uptake.
Life Sci. 105(1-2) , 31-42, (2014) Although acute hyperglycemic (AHG) episodes are linked to lower glucose uptake, underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We hypothesized that AHG triggers reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and inc... |
|
|
The effect of benfotiamine on mu-opioid receptor mediated antinociception in experimental diabetes.
Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 122(3) , 173-8, (2014) Diabetic neuropathy is a prevalent, disabling disorder. Currently, the only treatments available to patients with diabetic neuropathy are glucose control and pain management. B vitamin present neuropr... |
| berdi |
| S-benzoylthiamine monophosphate |
| bietamine |
| biotamin |
| S-[(2Z)-2-{[(4-Amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl](formyl)amino}-5-(phosphonooxy)-2-penten-3-yl] benzenecarbothioate |
| betivina |
| S-Benzoyl-thiamin-monophosphat |
| EINECS 245-013-4 |
| Benfotiamine |
| neurostop |
| S-Benzoylthiamine O-Monophosphate |
| 8088c.b. |
| Benfotiaminum |
| S-Benzoyl-thiamin-O-monophosphat |
| S-benzoylthiamine-O-monophosphate |
| MFCD00057343 |
| MilgaMMa |
| btmp |
| benzenecarbothioic acid, S-[(1Z)-2-[[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]formylamino]-1-[2-(phosphonooxy)ethyl]-1-propen-1-yl] ester |
| nitanevril |
| tabiomyl |