Benfotiamine
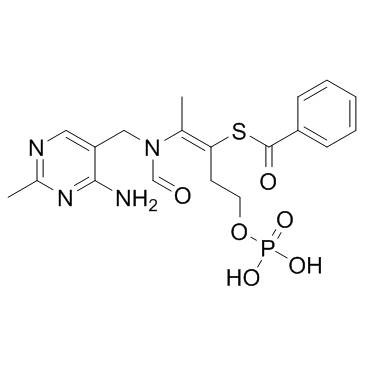
Benfotiamine structure
|
Common Name | Benfotiamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22457-89-2 | Molecular Weight | 466.448 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 745.1±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N4O6PS | Melting Point | 165ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 404.4±35.7 °C | |
|
Benfotiamine, a synthetic S-acyl thiamine derivative, has different mechanisms of action and a different pharmacological profile than lipid-soluble thiamine disulfide derivatives.
BMC Pharmacol. 8 , 10, (2008) Lipid-soluble thiamine precursors have a much higher bioavailability than genuine thiamine and therefore are more suitable for therapeutic purposes. Benfotiamine (S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate), an amphiphilic S-acyl thiamine derivative, prevents the prog... |
|
|
The detrimental effects of acute hyperglycemia on myocardial glucose uptake.
Life Sci. 105(1-2) , 31-42, (2014) Although acute hyperglycemic (AHG) episodes are linked to lower glucose uptake, underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We hypothesized that AHG triggers reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and increases non-oxidative glucose pathway (NOGP) activation, i.e... |
|
|
The effect of benfotiamine on mu-opioid receptor mediated antinociception in experimental diabetes.
Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 122(3) , 173-8, (2014) Diabetic neuropathy is a prevalent, disabling disorder. Currently, the only treatments available to patients with diabetic neuropathy are glucose control and pain management. B vitamin present neuroprotective effects, which are suggested to be related to thei... |
|
|
Boosting the pentose phosphate pathway restores cardiac progenitor cell availability in diabetes.
Cardiovasc. Res. 97(1) , 55-65, (2013) Diabetes impinges upon mechanisms of cardiovascular repair. However, the biochemical adaptation of cardiac stem cells to sustained hyperglycaemia remains largely unknown. Here, we investigate the molecular targets of high glucose-induced damage in cardiac pro... |
|
|
Advanced glycation end-products inhibition improves endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis.
Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 15(1) , 45-55, (2012) Chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with vascular endothelial dysfunction. The objective was to study the efficacy and safety of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) inhibitor (benfotiamine 50 mg + pyridoxamine 50 mg + methylcobalamin... |
|
|
Prostatic acid phosphatase is required for the antinociceptive effects of thiamine and benfotiamine.
PLoS ONE 7(10) , e48562, (2012) Thiamine (Vitamin B1) is an essential vitamin that must be obtained from the diet for proper neurological function. At higher doses, thiamine and benfotiamine (S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate, BT)-a phosphorylated derivative of thiamine-have antinociceptive... |
|
|
[A relationship between analgesic and neurotropic effects by the example of milgamma].
Ter. Arkh. 84(12) , 131-4, (2012) Combined vitamin preparations containing thiamine (vitamin B1), pyridoxine (vitamin B6), and cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) are widely used in medical practice. The results of investigations have confirmed that it is expedient to potentiate an analgesic effect ... |
|
|
[The optimization of the treatment of the vertebrogenic pain syndrome: neurotrophic treatment potentiates the effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs].
Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S. S. Korsakova 112(11) , 59-60, (2012)
|
|
|
[The importance of the pharmaceutical form and the routes of administration of B-group vitamins for the efficacious treatment of neurosensorial hearing loss].
Vestn. Otorinolaringol. (2) , 57-60, (2012) The objective of the present comparative study was to estimate the efficacy of the treatment of neurosensorial hearing loss (NSHL) with the use of milgamma, milgamma compositum, and vitamins B1 and B2 monotherapy. The best results were obtained after the trea... |
|
|
[Cochleovestibular disorders: approaches to diagnostics and treatment].
Vestn. Otorinolaringol. (5) , 55-8, (2011) The aim of this work was to evaluate the efficacy of introduction of milgamma and milgamma compositum in the treatment of 52 patients with cochleovestibular disorders of different etiology. Thirteen patients enrolled in the study received standard therapy and... |