Boc-L-phenylalanine

Boc-L-phenylalanine structure
|
Common Name | Boc-L-phenylalanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13734-34-4 | Molecular Weight | 265.31 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 426.6±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19NO4 | Melting Point | 85-87 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 211.8±26.8 °C | |
Use of Boc-L-phenylalanineBoc-L-phenylalanine is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Boc-L-phenylalanine is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 426.6±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 85-87 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 265.31 |
| Flash Point | 211.8±26.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 265.131409 |
| PSA | 75.63000 |
| LogP | 2.96 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
| InChIKey | ZYJPUMXJBDHSIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NC(Cc1ccccc1)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Transport and signaling via the amino acid binding site of the yeast Gap1 amino acid transceptor.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 45-52, (2009) Transporter-related nutrient sensors, called transceptors, mediate nutrient activation of signaling pathways through the plasma membrane. The mechanism of action of transporting and nontransporting tr... |
|
|
Investigation of dendriplexes by ion mobility-mass spectrometry.
Molecules 19(12) , 20731-50, (2014) Highly branched polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers presenting biological activities have been envisaged as non-viral gene delivery vectors. They are known to associate with nucleic acid (DNA) in non-co... |
|
|
NMR spectroscopic detection of chirality and enantiopurity in referenced systems without formation of diastereomers.
Nat. Commun. 4 , 2188, (2013) Enantiomeric excess of chiral compounds is a key parameter that determines their activity or therapeutic action. The current paradigm for rapid measurement of enantiomeric excess using NMR is based on... |
| N-tert-Butyloxycarbonyl-L-phenylalanine |
| Boc-phenylalanine |
| EINECS 237-305-5 |
| N-{[(2-Methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}-L-phenylalanine |
| Boc-L-Phenylalanine |
| (2S)-2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
| (2S)-2-({[(2-Methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}amino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
| N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanin |
| (S)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid |
| N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-L-phenylalanine |
| boc-L-Phe |
| L-Phenylalanine, N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]- |
| N-t-Butyloxycarbonyl-L-phenylalanine |
| L-Phenylalanine, N-((1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl)- |
| N-α-t-BOC-L-phenylalanine |
| N-Boc-L-phenylalanine |
| MFCD00002663 |
| Boc-Phe-OH |
 CAS#:63-91-2
CAS#:63-91-2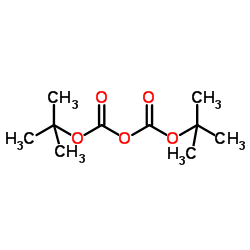 CAS#:24424-99-5
CAS#:24424-99-5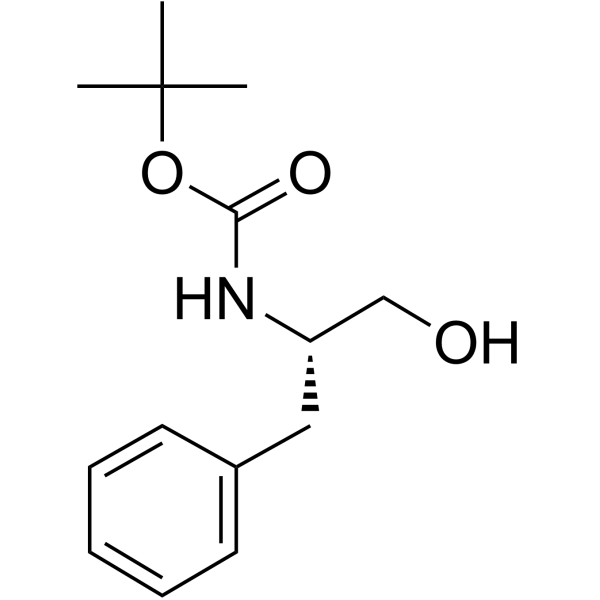 CAS#:66605-57-0
CAS#:66605-57-0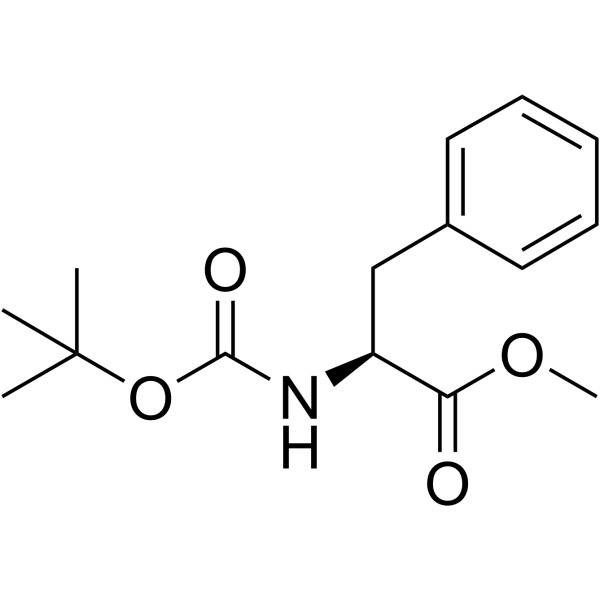 CAS#:51987-73-6
CAS#:51987-73-6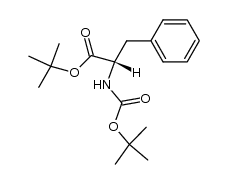 CAS#:116400-16-9
CAS#:116400-16-9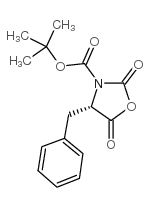 CAS#:142955-51-9
CAS#:142955-51-9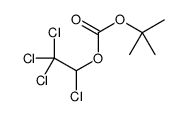 CAS#:98015-52-2
CAS#:98015-52-2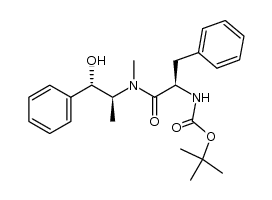 CAS#:185509-03-9
CAS#:185509-03-9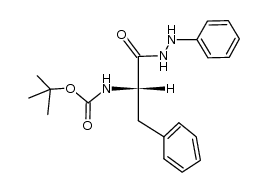 CAS#:17790-88-4
CAS#:17790-88-4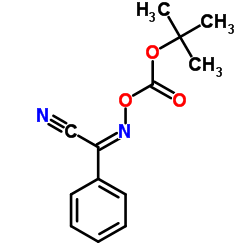 CAS#:58632-95-4
CAS#:58632-95-4 CAS#:3303-55-7
CAS#:3303-55-7 CAS#:37553-65-4
CAS#:37553-65-4 CAS#:37553-64-3
CAS#:37553-64-3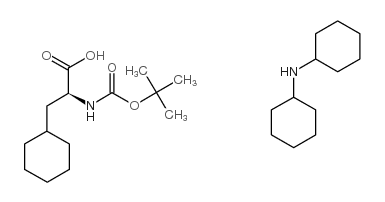 CAS#:37462-62-7
CAS#:37462-62-7 CAS#:33507-63-0
CAS#:33507-63-0![[Nle11]-Substance P structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/57462-42-7.png) CAS#:57462-42-7
CAS#:57462-42-7 CAS#:37736-82-6
CAS#:37736-82-6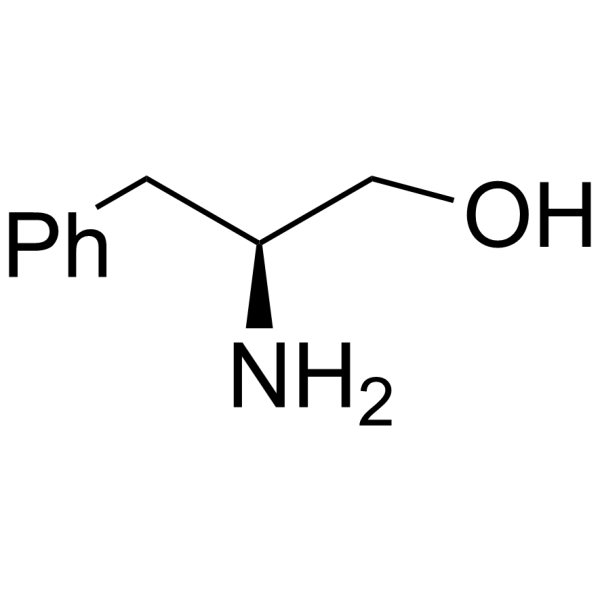 CAS#:3182-95-4
CAS#:3182-95-4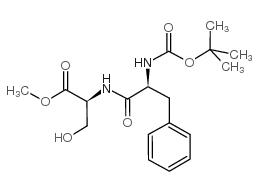 CAS#:34290-59-0
CAS#:34290-59-0 CAS#:33014-68-5
CAS#:33014-68-5
