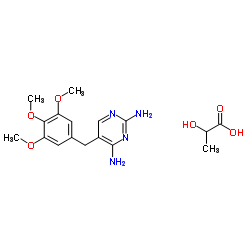
23256-42-0
| Name | Trimethoprim lactate salt |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-Hydroxypropanoic acid - 5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine (1:1)
EINECS 245-533-1 2,4-Diamino-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)pyrimidine lactate salt Trimethoprim lactate 2-hydroxypropanoic acid,5-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methyl]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine Propanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, compd. with 5-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-2,4-pyrimidinediamine (1:1) MFCD00171722 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid - 5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)-2,4-pyrimidinediamine (1:1) UNII:P3K8GP9FDQ |
| Description | Trimethoprim lactic is a bacteriostatic antibiotic and an orally active dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor. Trimethoprim lactic is active against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria. Trimethoprim lactic has the potential for urinary tract infections, Shigellosis and Pneumocystis pneumonia treatment[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Dihydrofolate reductase[1] Bacteria[1] |
| In Vitro | Trimethoprim interrupts folate metabolism by inhibition of the activity of dihydrofolase reductase (DHFR), which reduces dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate (THF)[1]. Trimethoprim causes protein aggregation and induction of main heat shock proteins (Hsps) in E. coli cells, which indicates that Trimethoprim presence leads to protein misfolding. Trimethoprim causes induction of DnaK, DnaJ, GroEL, ClpB, and IbpA/B Hsps. Among these Hsps, IbpA/B are most efficiently induced by Trimethoprim and coaggregates with the insoluble proteins. Upon folate stress, deletion of the delta ibpA/B operon resulted in increased protein aggregation but does not influence cell viability[1]. |
| In Vivo | In intraperitoneal infections in mice, the CD50 values for Trimethoprim alone against H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae, E. coli and N. meningitidis, is 150 mg/kg, 335 mg/kg, 27.5 mg/kg and 8.4 mg/kg, respectively[2]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 526ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H24N4O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 380.396 |
| Flash Point | 271.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 380.169586 |
| PSA | 163.04000 |
| LogP | 1.87180 |
| Vapour Pressure | 3.74E-11mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R43;R61 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37/39-S45-S53 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|