| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
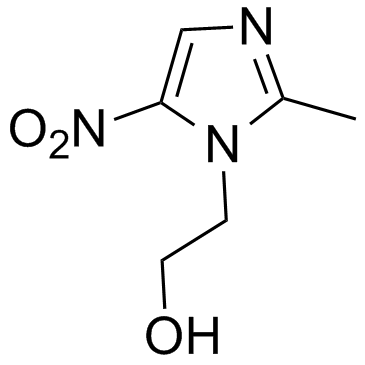 |
Metronidazole
CAS:443-48-1 |
|
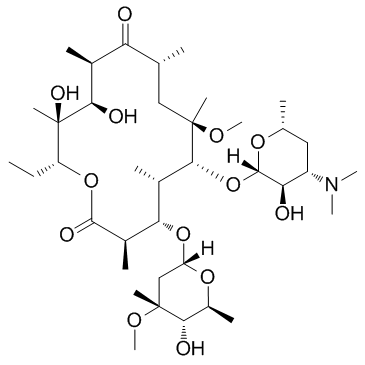 |
Clarithromycin
CAS:81103-11-9 |
|
 |
Rifaximin
CAS:80621-81-4 |
|
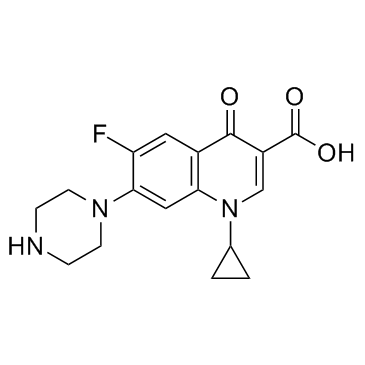 |
Ciprofloxacin
CAS:85721-33-1 |
|
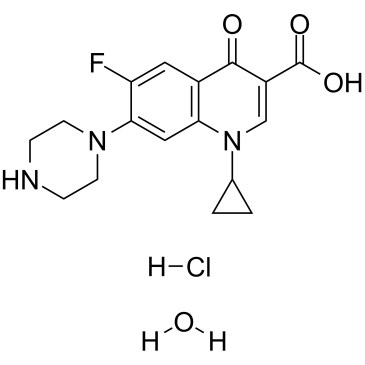 |
Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride hydrate
CAS:86393-32-0 |